Intel has officially launched its Xeon 600 Series processors for workstations, delivering the company’s most significant single-socket workstation platform update in years. Codenamed Granite Rapids-WS, the new lineup dramatically increases core counts, expands memory capacity and bandwidth, and introduces a new unified platform designed for sustained professional workloads.
Built on Intel 3 process technology and using Redwood Cove performance cores exclusively, Xeon 600 replaces the previous Xeon W-2500 and W-3500 families and consolidates Intel’s workstation offerings under one platform. With support for up to 86 cores, 172 threads, 4 TB of memory, and 128 PCIe Gen 5 lanes, Xeon 600 is positioned as Intel’s direct response to AMD’s Threadripper Pro 9000 series.
Unified Xeon 600 Platform Replaces Split Workstation Lineup
Unlike the previous generation, where Intel separated “mainstream” and “expert” workstation CPUs, all Xeon 600 processors now share a single platform based on the W890 chipset.
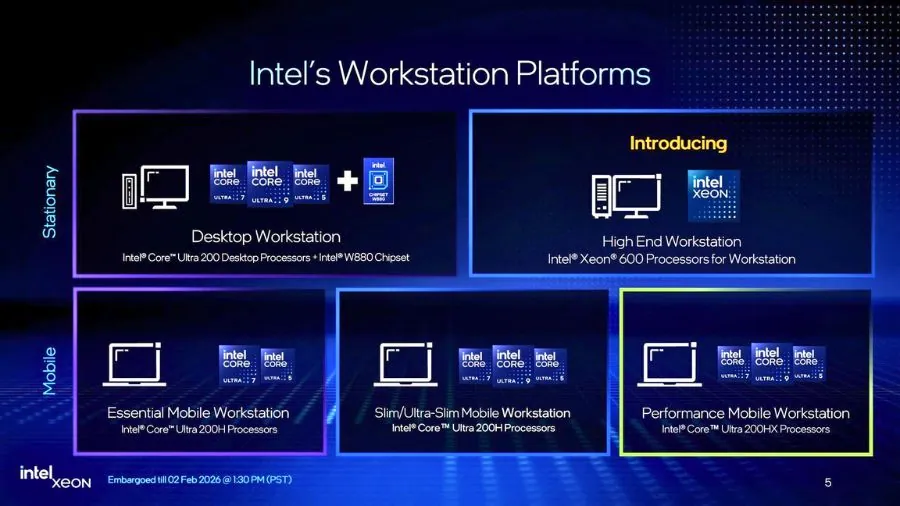
Key platform characteristics include:
- One socket, one chipset (W890)
- Performance cores only, no efficiency cores
- Hyper-Threading enabled across the stack
- Designed for sustained, predictable throughput rather than burst clocks
Intel says this design better aligns with workloads such as engineering simulation, rendering, scientific computing, data analytics, and AI development, where consistency, memory bandwidth, and I/O scale matter more than peak frequency.
Xeon 600 SKU Stack: 11 Models Scaling Up to 86 Cores
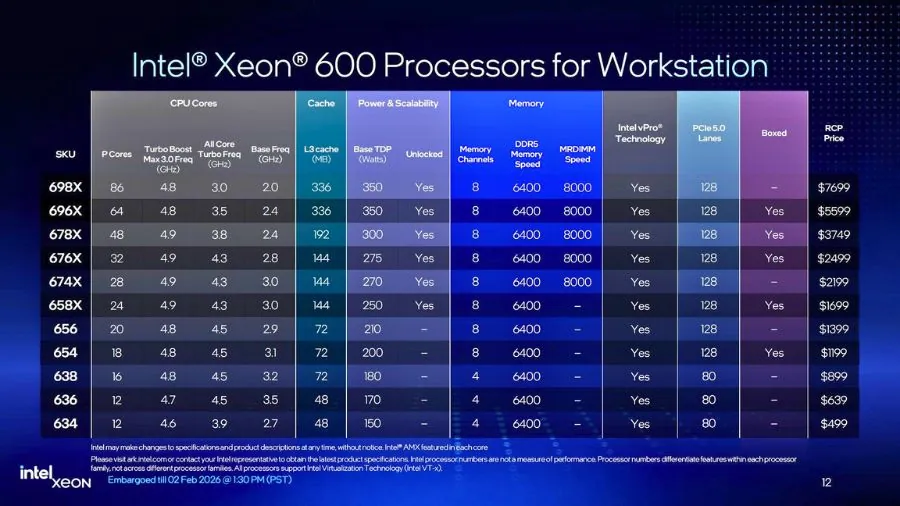
The Xeon 600 workstation family consists of 11 SKUs, ranging from entry-level 12-core parts to a new 86-core flagship.
Key Xeon 600 Workstation Specifications (Selected SKUs)
Xeon 698X (Flagship)
- 86 cores / 172 threads
- Base clock: ~2.0 GHz
- Max turbo: up to 4.8 GHz
- All-core turbo: ~3.0 GHz
- 336 MB L3 cache
- 350 W base TDP, up to ~420 W turbo power
- Fully unlocked (X-series)
Xeon 696X
- 64 cores / 128 threads
- Similar platform features with lower power and cost
Mid-range SKUs
- 48, 32, 24, and 20 cores
- Reduced cache and power limits
- Same platform I/O capabilities
Entry-level models
- 12-core and 16-core parts
- Target lighter workstation deployments and entry professional systems
Intel uses different die classes across the stack:
- XCC dies (dual compute tiles) for 86- and 64-core SKUs
- HCC dies for mid-range models
- LCC dies for lower-core processors
Intel confirmed that physical package and form-factor constraints prevented Granite Rapids-WS from scaling to the 128-core configurations used by some server-class Xeons.
Memory Architecture: 8 Channels, 2 DIMMs per Channel, Up to 4 TB
Memory capability is one of Xeon 600’s biggest differentiators.
Official memory support includes:
- Eight DDR5 memory channels
- Two DIMMs per channel
- DDR5-6400 RDIMM support across the lineup
- DDR5 MRDIMM support up to 8000 MT/s on select SKUs
- Maximum memory capacity of 4 TB per socket
What MRDIMMs Mean for Workstations
MRDIMMs (Multiplexed Rank DIMMs) use onboard multiplexers to combine multiple memory ranks, effectively increasing bandwidth without increasing channel count. While MRDIMMs have been used in data-center platforms, Xeon 600 is the first Intel workstation platform to support them.
Intel limits MRDIMM support to higher-end SKUs (starting around the 28-core class), stating that lower-core processors do not benefit meaningfully from the additional bandwidth. This approach reduces validation complexity while targeting memory-bound professional workloads such as finite-element analysis, AI model training, and large-scale 3D rendering.
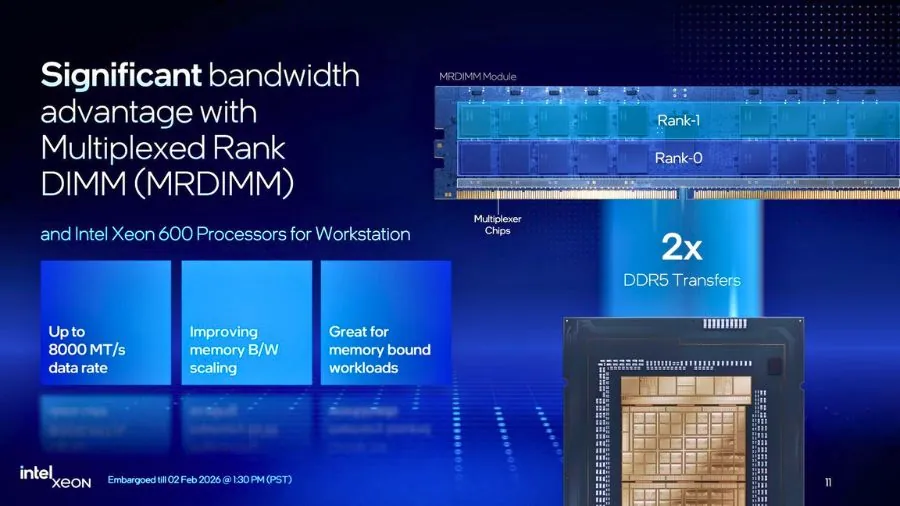
Compared to AMD’s Threadripper Pro platform, Xeon 600 supports twice the maximum memory capacity and two DIMMs per channel, giving Intel a clear advantage in extreme memory-heavy scenarios.
I/O Expansion: 128 PCIe Gen 5 Lanes and CXL 2.0
Every Xeon 600 workstation CPU provides:
- Up to 128 PCIe 5.0 lanes directly from the CPU
- CXL 2.0 support for future memory and accelerator expansion
- Native multi-GPU, storage, and networking support without PCIe switches
This allows workstation builders to deploy multiple GPUs, high-speed NVMe storage arrays, and high-bandwidth network cards with minimal latency and reduced platform complexity, which is especially important for AI development and data-intensive workflows.
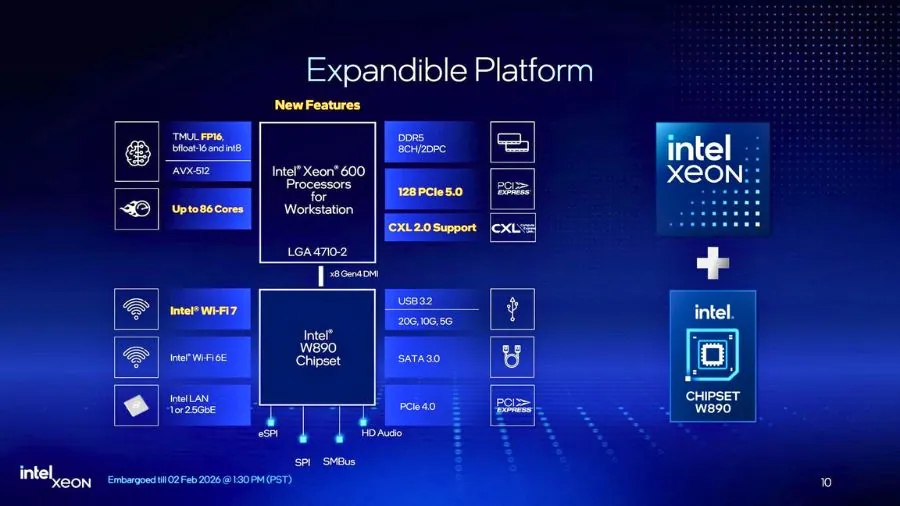
W890 Chipset and Platform Updates
Xeon 600 processors pair with Intel’s new W890 workstation chipset, replacing W790.
Platform updates include:
- Updated I/O routing and connectivity
- Integrated Wi-Fi 6E, with discrete Wi-Fi 7 support
- Validation for continuous, high-load professional environments
Intel says major OEMs and system integrators are already adopting W890 for upcoming single-socket workstation designs.
Overclocking Returns to Xeon Workstations

Select Xeon 600 processors with an “X” suffix are fully unlocked, marking a rare return of official overclocking support in the Xeon workstation lineup.
Supported features include:
- Unlocked multipliers
- Per-core and per-die tuning
- Fine-grained AVX and AMX ratio controls
- Expanded telemetry and protection mechanisms
- New undervolt and overvolt safeguards
Intel positions this capability for professional users and system integrators who need to tune systems for latency-sensitive or specialized workloads while remaining within a validated, warranty-backed platform.
Performance Claims and Architectural Focus
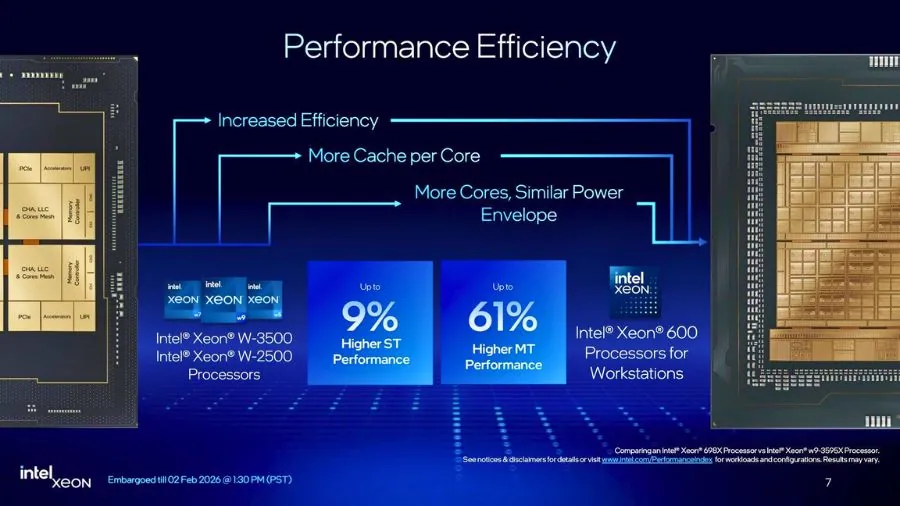
According to Intel, Xeon 600 delivers:
- Up to 9% higher single-thread performance
- Up to 61% higher multi-thread performance compared to prior Xeon workstation generations
These gains are attributed primarily to:
- Substantially higher core counts
- Larger L2 and L3 caches
- Increased memory bandwidth
- Architectural refinements rather than major IPC jumps
Intel has also expanded AMX (Advanced Matrix Extensions) with FP16 support, targeting AI training and inference workloads. However, Intel did not publish direct launch benchmarks against AMD’s Threadripper Pro 9000 series, meaning real-world comparisons will depend on independent testing.
Pricing and Availability
Pricing starts at approximately $499 for entry-level models.
The flagship Xeon 698X is priced at $7,699.
Only five SKUs will be available as boxed retail CPUs.
Higher-core models are primarily sold through OEM and system-integrator channels.
Intel expects W890-based workstation systems to begin shipping in late March 2026.
What Xeon 600 Means for the Workstation Market
With Xeon 600, Intel is clearly prioritizing scale, memory capacity, bandwidth, and I/O flexibility over desktop-style peak clocks. On paper, the platform offers one of the most capable single-socket workstation configurations Intel has ever delivered.
Whether Xeon 600 can reclaim share from AMD will ultimately depend on independent benchmarks, power efficiency, and real-world pricing. Still, for professionals running sustained, memory-intensive workloads, Xeon 600 significantly raises the ceiling of what a single-socket workstation can do.
Source: Intel




