When we talk about upgrading their computer, the focus usually goes straight to the processor, graphics card, or maybe storage. RAM is often mentioned quickly, but here’s the thing: not all RAM is the same.
Most of us are used to the standard type of memory that just stores and transfers data. But there’s a special type of memory called ECC RAM, and it works smarter.
So why should you care?
Because in some situations, a small memory error can cause big problems, like server crashes, database failures, even serious malfunctions in medical systems. And that’s where ECC RAM comes into play.
In this guide, we’re going to break down everything you need to know:
What is ECC RAM?
ECC stands for Error-Correcting Code RAM. It’s a special type of memory that not only stores information, but also checks for mistakes and corrects them.
The difference is-
Normal RAM stores data exactly as it’s given, without checking whether it’s right or wrong.
ECC RAM stores data with additional checking bits. When the system reads that data again, those checking bits are used to verify whether everything matches. If a small error is found, it’s immediately corrected before it even reaches the processor.
These small errors, called single-bit errors, are much more common than people think. They can be caused by electrical interference, high temperatures, faulty hardware, or even natural background radiation.
In a home computer, such errors may go unnoticed or may only cause program crashes. But in a server or any critical system, a single wrong bit can cause data loss, corrupted files or downtime.
That’s why ECC RAM is mainly used in systems where reliability is more important than raw speed. It ensures that data stays accurate and prevents silent memory errors from turning into major failures.
Also Read: What is RAM? Everything You Need to Know
History of ECC RAM
Before ECC RAM, computers used a type of memory called parity RAM. This type of memory could only detect errors, not correct them. If a bit was reversed, the system would crash or data would be corrupted.
As servers began to run more stably and handle more demanding tasks, this became a major problem. That’s when ECC RAM came into the picture. It could detect and correct single-bit errors, making systems much more stable.
By the late 1990s, ECC RAM became common in servers and workstations, especially in CPUs such as Intel Xeon and AMD EPYC. Even today, these processor families support ECC in data centers and professional systems.
A Brief History of RAM Development
| Year/Period | RAM Type | Key Feature | Limitation | Role in ECC History |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970s–1980s | DRAM (Dynamic RAM) | First widely used memory in PCs | No error detection, vulnerable to bit flips | Early base memory |
| 1980s–1990s | Parity RAM | Added 1 parity bit to check for errors | Could detect but not fix errors | Predecessor to ECC |
| Early 1990s | ECC RAM introduced | Error detection and correction | Slightly slower and more expensive | Became standard in servers |
| Late 1990s–2000s | DDR SDRAM | Faster double data rate memory | Consumer DDR lacked ECC in most PCs | ECC used in DDR for servers |
| 2010s–Present | DDR3/DDR4/DDR5 with ECC | Supports advanced workloads in servers | Higher cost, limited to specific CPUs/boards | Current ECC standard |
How Does ECC RAM Work?
ECC RAM works by adding extra bits of information whenever data is stored in memory. These bits are not part of the original data but are used for checking accuracy. When the processor later retrieves that data, the memory controller compares the stored checking bits with the actual data bits.
ECC RAM Working steps:
Step 1: Writing Data – When information is written into ECC RAM, additional error-checking bits are generated and stored along with the data.
Step 2: Checking During Read – When the data is read back, the system compares it against the error-checking bits.
Step 3: Detecting Errors – If a mismatch is found, the system identifies which bit is incorrect.
Step 4: Correcting Errors – For single-bit errors, the system corrects the mistake immediately without the user noticing anything.
Step 5: Flagging Bigger Issues – If there’s a double-bit error, ECC RAM cannot fix it but can at least detect it and alert the system.
From a technical perspective, for every 64 bits of actual data, ECC RAM generates an additional 7 or 8 bits as error-correcting data. This allows it to run a mathematical check, called a parity or Hamming code, to ensure that everything is accurate.
Since this process is continuous, ECC RAM is constantly monitoring and protecting system memory. Its impact on performance is minimal, but the increase in reliability is significant, which is why it is trusted in servers, data centers, and other mission-critical environments.
According to large-scale studies, memory errors are more common than most users realize. Research cited by Wikipedia found that up to 8% of DIMMs experience at least one memory error per year. Puget Systems also reported that systems with ECC RAM showed failure rates of only 0.24% compared to nearly 1% for non-ECC setups.
Who Needs ECC RAM?
ECC RAM is not designed for everyone. It is mainly used where accuracy, stability, and reliability matter more than speed or cost.
1. Servers and Data Centers
Servers run nonstop, handling thousands of requests and managing critical databases. Even a single memory error can bring down services, corrupt customer data, or cause costly downtime. That’s why large data centers and cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud always use ECC RAM to keep their systems stable.
2. Healthcare and Research Systems
In hospitals, laboratories, and scientific research, accuracy is critical. A corrupted bit in a medical scan or a genetic sequence could lead to a wrong diagnosis or a failed experiment. ECC RAM ensures that data in these systems remains accurate, reducing the risk of dangerous mistakes.
3. Aerospace, Defense, and Airlines
In industries where safety is everything, reliability cannot be compromised. Aircraft systems, defense technologies, and aerospace equipment often run on ECC memory to prevent even the smallest chance of system failure.
4. Network-Attached Storage (NAS) and RAID Servers
Storage systems that keep large volumes of data for businesses and individuals also benefit from ECC RAM. Without it, stored data can slowly degrade over time due to tiny memory errors, a problem often called “bit rot.” ECC RAM helps prevent that and keeps long-term data safe.
For example, filesystems like ZFS are designed to ensure long-term data integrity. However, TrueNAS experts warn that without ECC RAM, ZFS cannot protect against memory-induced corruption, leading to silent ‘bit rot.’ This is why ECC RAM is considered essential in NAS setups.
5. Professional Workstations
High-end workstations used for 3D rendering, financial modeling, and engineering simulations often use ECC RAM. These tasks involve large calculations and datasets where accuracy is more important than saving a few milliseconds of speed.
6. Gamers and Everyday PC Users
For most people, ECC RAM is unnecessary. Gaming PCs, home desktops, and laptops do not need it because a memory error in these systems usually just causes a crash or freeze — inconvenient, but not disastrous. Non-ECC RAM is faster, cheaper, and works perfectly fine for personal use.
Industry professionals have debated ECC memory for years. Jeff Atwood from Coding Horror pointed out that the price difference between ECC and non-ECC memory has become minimal, making it harder to justify skipping it in professional setups. Similarly, sysadmins in TrueNAS forums often report that ECC saved them from silent data corruption in storage servers — issues that would have gone undetected with standard RAM.
Section 5: ECC RAM vs Non-ECC RAM
When comparing ECC RAM with regular (non-ECC) like DDR4, or DDR5 RAM, the main differences come down to reliability, cost, and use cases.
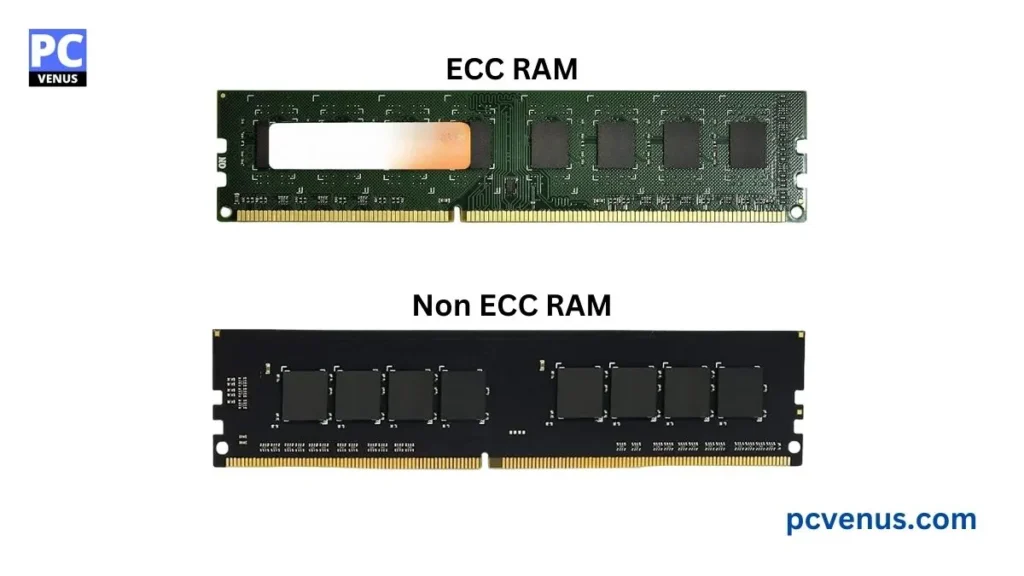
| Feature | ECC RAM | Non-ECC RAM |
| Error Detection & Fix | Detects and corrects single-bit errors | No error detection or correction |
| Reliability | Very high, prevents crashes and corruption | Standard, may crash if errors occur |
| Speed | Slightly slower due to error checking | Faster since no extra checks |
| Cost | More expensive | Cheaper |
| Compatibility | Supported by server/workstation hardware | Supported by most consumer hardware |
| Best Use Cases | Servers, workstations, data-critical tasks | Gaming, everyday PCs, laptops |
Benchmark tests from Puget Systems showed ECC RAM to be about 0.7% to 2.2% slower than non-ECC RAM. Crucial also notes a typical 2–3% performance drop. For most workloads, this difference is negligible, but it’s worth knowing when comparing options.
Quick Summary of the differences between ECC RAM vs Non-ECC RAM
- ECC RAM is based on consistency and data integrity. It is slow and expensive, but it ensures that data remains accurate, making it a must-have for professional and enterprise systems.
- Non-ECC RAM is about speed and affordability. It is perfect for gamers, home users, and anyone who doesn’t need error correction.
Pros and Cons of ECC RAM
Like every component, ECC RAM has its strengths and weaknesses. Here’s a balanced look at both:
Pros of ECC RAM
- Detects and fixes single-bit errors automatically.
- Improves system stability and prevents crashes.
- Protects data from silent corruption.
- Essential for servers, healthcare, finance, and research.
Cons of ECC RAM
- More expensive than regular RAM.
- Slightly slower due to error-checking.
- Works only with specific CPUs and motherboards.
- No benefit for gaming or everyday PC use.
Is ECC RAM Worth It?
Whether ECC RAM is worth buying depends entirely on how the system will be used. It is not a one-size-fits-all upgrade.
When ECC RAM is Worth It
Servers and Data Centers: Constant uptime and stability are more important than speed. ECC RAM prevents downtime and data corruption, which could otherwise cost businesses millions.
Healthcare and Research: Accuracy is critical. A single data error in a medical scan or genetic sequence could lead to serious mistakes.
Aerospace and Defense: Systems must operate without failure, where even small memory errors could cause life-threatening problems.
Professional Workstations: Used for 3D modeling, simulations, financial analysis, or large-scale calculations where precision matters. If you’re building a workstation, consider options like best 32GB RAM laptops or 64GB RAM laptops instead of ECC RAM unless your work demands absolute reliability.
It’s important to note that ECC RAM will only provide error correction if both the CPU and motherboard support it. If installed in a non-ECC system, it will usually run as normal RAM without error correction. As Crucial explains, some boards even treat ECC RAM as standard memory by default, so always check compatibility before buying.
When ECC RAM is Not Worth It
- Gaming PCs: ECC RAM does not improve frame rates or make games smoother.
- Everyday Users: Browsing, streaming, office work, and school tasks do not benefit from ECC RAM.
- Budget Builds: Since ECC RAM is more expensive and slower than non-ECC RAM, it’s not practical unless accuracy is a priority.
How to Check if Your System Supports ECC RAM
Not every computer can take advantage of ECC memory. Even if you buy ECC RAM sticks, they will only work as standard non-ECC RAM if your CPU and motherboard don’t support error correction. Here’s how you can check:
1. Check the CPU Specifications
- Most Intel Xeon and some Intel Core i9/i7 workstation models support ECC RAM.
- On the AMD side, EPYC, Ryzen Pro, and Threadripper Pro processors typically support ECC.
- You can confirm by looking up your CPU model on the Intel ARK database or AMD’s product page.
2. Check the Motherboard Specs
- ECC compatibility is usually listed in the motherboard manual or product page.
- Server and workstation boards almost always support it, while consumer motherboards usually don’t.
- If you’re building a system, pair a Xeon or EPYC processor with a board designed for ECC.
3. Use System Tools (for Existing PCs)
- Windows: Tools like CPU-Z or HWiNFO can show if ECC is detected and enabled.
- Linux: Run the command
dmidecode -t memoryand look for an “Error Correction” field. If it says “Single-bit ECC,” your system supports it.
4. Check With the Manufacturer
When in doubt, contact the system or motherboard manufacturer. They can confirm whether ECC RAM will actually run with error correction on your setup.
FAQs
1. Does ECC RAM improve gaming performance?
No. ECC RAM does not increase FPS or make games smoother. Gaming systems gain no performance benefit from ECC memory.
2. Can I use ECC RAM in a regular motherboard?
Only if the CPU and motherboard support it. Most consumer-grade motherboards and processors do not support ECC RAM.
3. Is ECC RAM slower than non-ECC RAM?
Yes, but only slightly. The difference is small and not noticeable in everyday use. The trade-off is much higher reliability.
4. Can ECC RAM prevent all memory errors?
No. It corrects single-bit errors and detects double-bit errors, but it cannot fix every possible memory issue.
5. Who should buy ECC RAM?
Businesses, researchers, data centers, and professionals who cannot risk data corruption should use ECC RAM. Regular PC users and gamers do not need it.
Final Words
ECC RAM is not made for everyone, and that is what makes it different from normal memory. It is extremely important for servers, workstations and industries where accuracy and reliability matter more than speed or cost. In these situations, a single memory error can lead to downtime, corrupted data or even critical failures – and ECC RAM provides protection against this.
On the other hand, for gamers, students or everyday PC users, it offers no real advantage. It will not improve performance or the gaming experience, and will only add unnecessary costs.
The Best notes is:
- If your system works on a workload where even a small error can cause problems, choose ECC RAM.
- If you just need a reliable PC for personal use, non-ECC RAM is enough. For everyday users, regular SO-DIMM RAM in laptops or DDR5 RAM in desktops is more than enough