The first computers used things like magnetic tape and punched cards to store their data. But in the last few years, there have been many changes in data storage. Magnetic tape and punched cards were followed by hard disk drive (HDD) storage, which was a huge improvement in the field of data storage as it provided larger storage capacity and faster access times than its predecessors, which became the standard storage for everyone for some time.
But now, Solid State Drives (SSD) are used as storage. It is much faster than all the old storage and uses advanced technology. They use NAND Flash special memory to store data, which makes them faster and more efficient.
Nowadays, in the computer Era, everyone wants speed, but this speed does not indicate how powerful your computer is, but rather how quickly the computer finds information. Traditional hard drives have rotating parts, which makes them slow. But there is nothing in SSDs that makes them lightning-fast. Due to this, the computer performs tasks like opening apps or loading files faster.
SSDs don’t have rotating disks inside like older hard drives. Instead, it uses NAND flash memory. Due to this, it is extremely quick and reliable. SSDs come in different shapes and sizes to meet different needs. They exist for everything from regular laptops to super-powerful servers. SSDs are making our computers faster, more durable, and better for the environment.
What is an SSD?
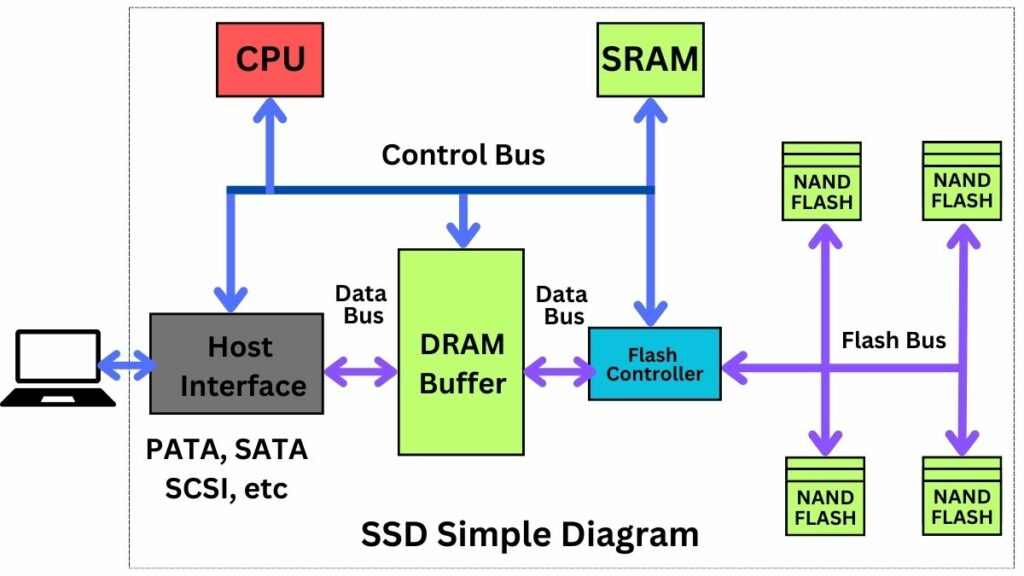
SSD stands for Solid State Drive, a modern computer storage drive. It provides modern storage in place of HDD. HDDs use spinning disks and mechanical parts to read and write data, but SSDs do not have any spinning disks and mechanical parts. Instead, they use NAND flash memory.
NAND flash memory has no moving parts, which helps SSDs access and transfer data much faster than HDDs. It is also more durable, reliable, and energy-efficient.
Types of SSDs
1. SATA
SATA is a type of SSD storage. They connect to the computer’s motherboard using a SATA interface like traditional hard disk drives but are much faster than HDDs. It reads and writes data faster than HDDs but slower than NVMe SSDs.
2. NVMe

NVMe is a type of SSD storage with a newer and more advanced interface designed specifically for SSDs. It connects directly to the motherboard via the PCIe bus, transferring data faster than SATA.
They transfer data much faster, resulting in top-level performance. It’s especially great for large file transfers, video editing, and gaming tasks.
3. PCIe
PCIe is a type of SSD storage that provides a high-speed interface. These connect directly to the motherboard through the PCIe slot. Due to its high speed, it is used in high-end laptops and desktops.
PCIe SSDs include both SATA and NVMe drives. NVMe SSDs using PCIe provide the highest performance among consumer SSDs.
How SSDs Work
NAND Flash Memory
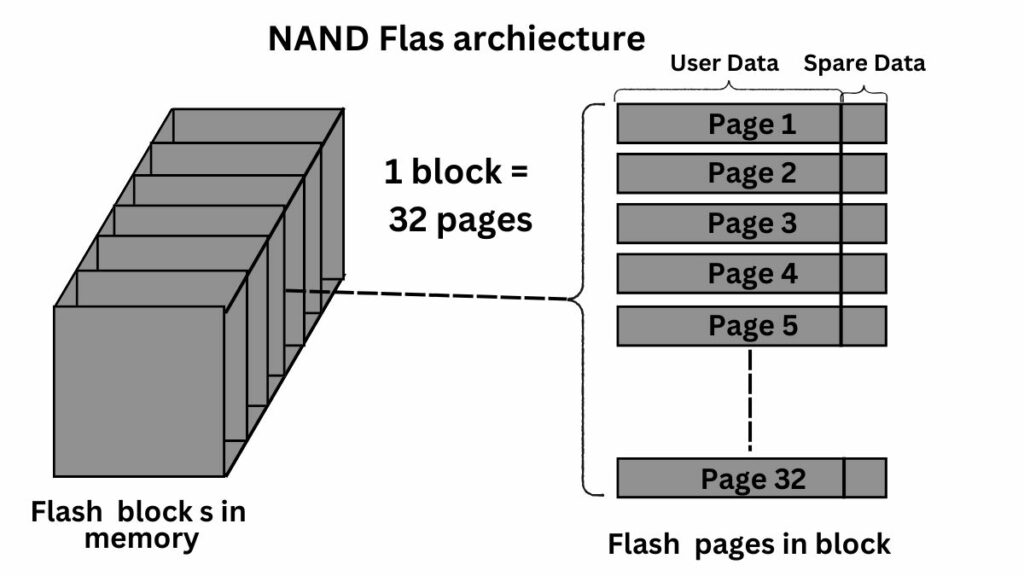
An SSD’s primary storage component is non-volatile NAND flash memory. Non-volatile means it retains data even when the power is turned off.
NAND flash consists of multiple memory cells further grouped into pages and blocks. Each cell has a floating gate that traps electrons, representing a charged state (1). When empty (0), there are no electrons in the gate. This binary code stores data efficiently.
Controller and firmware
SSDs have a controller; this is the vital component of SSDs that acts as the brain of the drive. It plays a vital role in overseeing the storage and retrieval of data within the SSD.
The controller manages data storage, retrieval, and communication with the computer’s operating system. When new data needs to be written to the drive, the controller determines where it should be stored in the NAND flash memory.
Firmware is software embedded in the SSD’s controller. Within the architecture of Solid State Drives (SSD), it stands out as the unsung hero, silently organizing and optimizing various operations.
Reading and Writing Data
The read process is triggered when the computer requests specific data stored on the SSD. The controller of the SSD receives the request, and then it communicates with the firmware to locate the exact address of the requested data within the NAND flash memory.
When the location is known, the controller activates the corresponding memory cells where the data is stored. The activated cells release their stored electrons, and the controller reads the electrical charge. This information is then converted into readable data and transmitted to the computer’s operating system.
When data needs to be stored, the SSD receives a write request from the computer’s operating system. In coordination with the firmware, the SSD’s controller identifies memory blocks available to store new data.
If the selected memory block contains existing data, the SSD’s controller begins erasing that block before writing new data. The controller writes new data into the memory cells by adjusting the charge. After new data is written, the SSD’s controller updates its mapping tables to track where it is stored.
Wear leveling
Wear leveling in a solid-state drive (SSD) distributes writes evenly across all of the NAND flash cells in the drive. Individual flash cells can withstand only a limited number of writes before they degrade, which helps increase the lifespan of SSDs.
Wear leveling helps extend the lifespan of an SSD by ensuring that all flash memory cells are used equally. This is done by dynamically mapping writes to different cells so that no one cell is written more frequently than others. It helps protect cells from premature damage.
Garbage collection
Garbage collection maintains optimal performance by reclaiming space on the SSD. Over time, when data is deleted or modified, the SSD does not immediately erase the corresponding cells, causing it to become fragmented on NAND flash memory. Due to this, there is a possibility of a decline in performance. Garbage collection identifies and consolidates these invalid pages, freeing up space for new data.
Advantages of SSDs
Faster performance
SSD is much faster than traditional HDD. It has faster reading and writing capabilities than HDD. Due to its fast speed, the computer boots quickly, programs launch very quickly, and files open instantly. Which makes the entire system feel faster and more responsive.
Improved durability and Reliability
SSDs have no moving parts like HDDs, making them more resistant to physical shocks and vibrations. That is why it is more durable and reliable.
Lightweight and compact
SSD does not have many physical parts, like HDD, which has parts like a platter, spindle, actuator, etc. Due to this, it is smaller and lighter than HDD.
Less power consumption
SSDs don’t have anything to do with rotating the disk or moving mechanical components like a traditional HDD. Due to this, it consumes less electricity. That is why it is mostly used in laptops and portable devices.
Silent Operation
HDD has a rotating disk, which makes it more noisy. Since SSDs have no moving parts, they operate silently.
Disadvantages of SSDs
Significantly Cost is High
SSDs are more expensive than traditional HDDs. Because NAND flash memory is the primary storage in SSDs, the manufacturing process is more complex and expensive than manufacturing the mechanical components of an HDD.
Difficult To Data Recovery
Data on SSDs is often overwritten more often than HDDs, making it harder to recover lost information. SSDs use NAND flash memory to store data, which consists of cells and complex electronic circuits that require specialized equipment and expertise to retrieve the data.
Limited Lifespan
NAND flash memory has a limited number of write cycles before it degrades. To increase the lifespan of an SSD, wear leveling algorithms are used that distribute write and erase cycles evenly across all memory cells, which prevents specific cells from wearing out faster than others. Still, its lifespan is less than that of HDDs.
Limited Capacity
SSD has less storage capacity than HDD. Although SSD capacities have increased over the years, they still do not reach the same level as HDDs.
Compatibility Issues
SSDs are generally compatible with most modern systems available today but may not be compatible with older hardware that does not have SATA or PCIe interfaces.
Applications of SSDs
Desktops and laptops
SSDs provide faster boot times and quicker application launches and simplify the process of transferring data between devices. Due to this, it is used in desktop computers, which provides a better overall system response.
Many laptops come with built-in SD card readers, allowing you to add additional storage space without opening the device. Also, it is more compact and lighter, which is why it is used in devices like laptops and ultrabooks.
Gaming Consoles
Games stored on SSD load faster than HDD. It also improves the performance of the entire game. SSDs help reduce or eliminate texture pop-in, a phenomenon where low-quality textures are initially displayed and then replaced with higher-quality versions as the game progresses.
SSDs are used in modern gaming consoles, such as the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X/S, due to their fast restart and seamless multitasking capabilities.
Smartphones and tablets
SSD’s fast read and write speeds result in faster app launches and faster data access and also consume very little power.
Apart from this, it is compact and lightweight, which is very important for smartphones and portable devices; that is why it is used in smartphones and tablets.
Video Editing and Rendering
SSDs have much faster read and write speeds than traditional HDDs, allowing video editing software and large multimedia files to load quickly. Additionally, it quickly transfers large video files between storage locations.
Due to the speed of SSD, rendering takes much less time. Its faster read and write speeds allow the software to access and process data more quickly, resulting in faster rendering of edited video projects. Due to the fast capacity of SSD, it is used in Video Editing and Rendering.
Cloud Computing
SSD is used in cloud computing for faster data access, lower latency, better scalability, and improved overall cloud infrastructure performance.
How To Choose the Right SSD
The price of SSDs varies greatly depending on their capacity, performance, and features. Set a realistic budget based on your needs and compare the prices of different models to find the best value for your money.
Before buying SSDs, consider your requirements as to how much storage you need. You may need an SSD with less storage, and buying an SSD with more storage can be a waste of your money. I recommend getting an SSD with a little more storage, as it may come in handy in the future.
Nowadays, many companies like SanDisk, Samsung Electronics, Intel,
SK Hynix, etc., makes SSDs, and the company matters a lot because a good company uses good materials to make SSDs; hence, before buying SSDs, find out which company’s SSD is good and cheap.
SSDs come in various sizes, such as 2.5-inch, M.2 SATA, and M.2 NVMe. Before buying it, check which SSD will fit in the slot of your device.
While buying an SSD, please pay special attention to its interface as it comes with different interfaces like SATA III M.2 NVMe. SATA III provides good performance, but M.2 NVMe SSDs use the PCIe bus for much faster speeds, which is ideal for demanding applications.
Some SSDs come with additional features, so choose the SSD that provides additional features in the same price range. With this, you can get a better SSD in the same price range.
SSD vs other storage
SSD vs HDD
| Feature | Solid State Drive (SSD) | Hard Disk Drive (HDD) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Durability | More durable | Less durable |
| Reliability | More reliable | More prone to failure |
| Size | More compact | Bulkier |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Power Consumption | Less | High |
| Noise | Silent | Audible |
| Cost | Expensive | Cheaper |
| Capacity | Available Up to 8 TB | Available in larger capacities |
| Fragmentation | No performance impact due to fragmentation | Can experience performance impact with fragmentation |
Also Read: SSD vs HDD: What’s the Difference?
SSD vs eMMC

| Features | SSDs (Solid State Drive) | eMMC (Embedded Multimedia Card) |
|---|---|---|
| Form factor | More Spacious | Compact |
| Power consumption | Requires More Power | More Efficient |
| Cost | Costlier | Economical |
| Performance | Comparatively Faster | Relatively Slower |
| Capacity | More | Less |
Also Read: What is eMMC: Everything You Need to Know
Final Word
SSDs have much faster read and write speeds than traditional HDDs, resulting in faster system response and less time for applications to load. SSD has no moving parts, which makes it more durable and resistant to physical shocks and vibrations. This work consumes electricity because it does not have spinning disks and mechanical parts like HDD, which consumes a lot of electricity.
SSDs are suitable for portable devices due to their compact size, low weight, and resistance to physical shocks,
It is lightweight and compact, making it great for laptops, tablets, and portable devices. Also, there is no mechanical part in it, so it does not make noise.
SSD makes multitasking much faster, and boot time is much less. Apart from this, it does not overheat while doing heavy work, due to which the system always remains cool.
People like SSDs a lot for data storage. Its use is continuously increasing, due to which in the coming time, people will abandon HDD and go for SSD only as SSD is set to become the dominant storage technology for personal computers and various other applications.
FAQs
Solid-state drives (SSD) are much faster than hard disk drives (HDD) because they do not have moving parts such as a spinning magnetic disk or spindle motor. But it comes with less storage compared to HDD and is also more expensive.
As there are moving parts in HDD, whose rapid rotation and mechanical wear generate heat due to which the HDD gets heated again and again.
Due to its thermal problems, it becomes sensitive to damage from vibrations, drops and shocks. Due to which its durability is greatly reduced. As a result, HDDs become less reliable for long-term storage and may fail prematurely.
The drawback of SSDs is their limited number of write cycles. This reduces the lifespan of SSDs. But nowadays advanced technologies like wear leveling and overprovisioning are employed in enterprise-class SSDs to increase their durability and support long-term use.
It is important to identify the types of SSDs because different types use different interfaces to send data. Although SSDs come in many types, the major ones are SATA, NVMe, and PCIe SSDs which are mostly used.
SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds than HDDs. There are no moving parts inside it, due to which its durability is high. The absence of any moving parts means that the risk of physical damage to the SSD is less. SSDs operate quietly due to the lack of moving components.
Also, it consumes less power, due to which the battery life of the laptop becomes longer. SSDs operate quietly due to the lack of moving components.




