Nowadays, electronic devices are developing rapidly, and storage is becoming essential as it plays an important role in shaping their functionality and efficiency.
For storage solutions, HDD was provided in the device for a long time, but now SSD has been replaced because its performance is much better than HDD and is more secure.
While SSD has replaced HDD, it is not for those devices that are small, light, and thin. To overcome this problem, eMMC storage is used, which does not come with much storage but is integrated into the circuit of the device, which does not require any separate physical space. It provides a compact and efficient solution to storage requirements.
What is eMMC?
The full form of eMMC is an Embedded Multimedia Card. It is non-volatile flash storage that integrates with the device. The MMC interface facilitates communication between the eMMC storage and the device’s processor.
It combines NAND flash memory, a controller, and a multimedia card (MMC) interface into a unified package, allowing it to be used in space-limited devices such as smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, and other embedded systems.
Importance of eMMC in modern electronic devices
Compact
eMMC NAND flash memory integrates the controller and interface into a single package and occupies minimal space. That is why it is used in thin and portable devices like smartphones, tablets, and ultra-thin laptops because these devices do not have much physical space.
Budget-Friendly
Devices with eMMC storage are more budget-friendly than devices with SSD storage. eMMC storage is installed in devices that do not have a high budget.
Power Savings
eMMC consumes very little battery as its architecture is designed for energy efficiency, resulting in longer battery life for devices that run on direct battery, such as smartphones and tablets.
Reliability and Durability
eMMC has features like wear leveling and error correction that make the storage even more reliable and durable. It is very beneficial for factories and cars as it does not break easily and works well.
User Experience
It has fast read and write speeds but not as much as SSD, but it still provides satisfactory performance in everyday tasks as the device runs smoothly and has a fast response.
Understanding eMMC
Origin of eMMC
Flash memory means that it retains its data even when there is a power failure. This is unlike the RAM because it also loses its data when there is a power failure, which is commonly used in mobiles, tablets, thin electronic devices, and other embedded systems. eMMC is good for all this because it is small, which makes it easy to fit into these small devices, and it is also fast and cheaper than other storage.
eMMC was first developed by JEDEC and the MultimediaCard Association in 2006.
Evolution from traditional storage
Performance
People were using the hard disk drive (HDD) as traditional storage; it had good capacity and a budget-friendly price, but it was slow, heavy, and took up a lot of space. Now, SSD has replaced the HDD; it’s a bit expensive but offers much faster performance and is more compact.
Manufacturers use eMMC as embedded storage. eMMC, a non-volatile memory based on NAND flash memory, is faster and more durable than traditional flash memory. This has led to the increased use of eMMC in recent years, especially for HD video playback and gaming.
Capacity
The capacity of traditional storage devices has increased significantly. HDDs come with up to 10 TB of storage, while SSDs come with up to 8 TB of storage. The capacity of eMMC devices has also continued to increase. Earlier its capacity was only a few GB, but now it comes with a capacity of up to 256 GB.
Features
Traditional storage devices have limited features. HDDs and SSDs only have basic data storage and retrieval capabilities.
eMMC devices offer a variety of features compared to traditional storage devices. Apart from basic data storage and retrieval, it also comes with secure boot, encryption, and wear leveling, making it considered to be a more versatile and secure storage mind.
Key components and structure
1. NAND flash memory
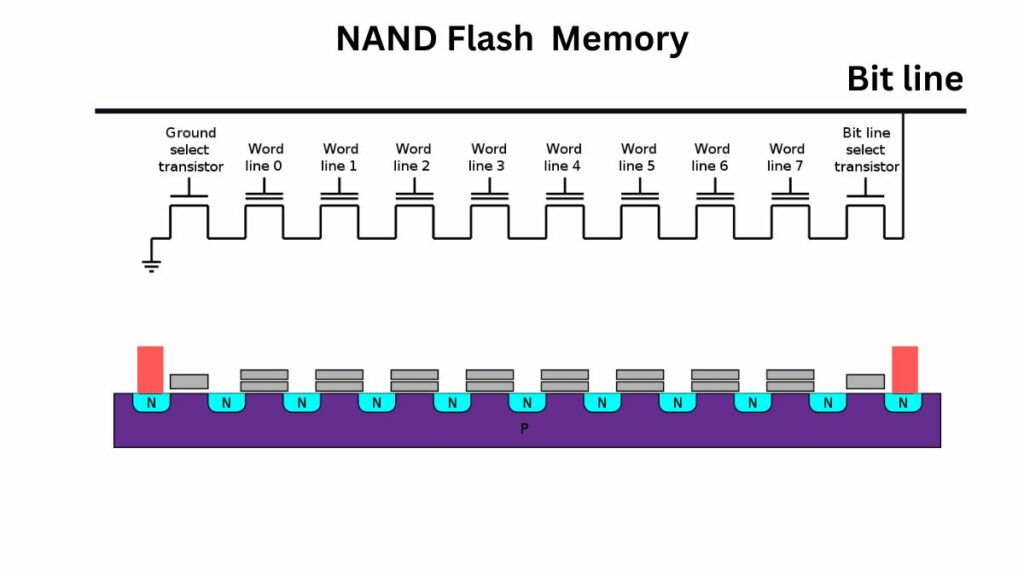
NAND flash memory is the storage medium of eMMC, which is non-volatile memory. This means it retains data even when there is a power failure, whereas volatile memory does not.
2. Controller
The controller is the chip of eMMC, which acts as the brain of eMMC. It manages the data flow between the NAND flash memory and the device’s processor. It handles tasks like reading, writing, error correction, and wear leveling.
3. MMC interface
The MMC interface is a communication link that connects the memory card to the host device via a serial interface that is a low-pin-count, high-speed interface, which facilitates data transfer between storage and device.
4. Integrated Package
Traditional storage consists of separate components, whereas eMMC integrates the NAND flash memory, controller, and MMC interface into a single compact package. Due to this, it is useful for those devices which have less physical space.
eMMC vs other storage
eMMC vs SSDs

| Features | eMMC(Embedded Multimedia Card) | SSDs(Solid State Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Form factor | Compact | More Spacious |
| Power consumption | More Efficient | Requires More Power |
| Cost | Economical | Costlier |
| Performance | Relatively Slower | Comparatively Faster |
| Capacity | Less | More |
Performance
eMMC is slightly slower than SSD, which makes it suitable for everyday tasks but not as good for heavy applications and tasks.
SSD is faster than eMMC and provides faster read and write speeds. Because the NAND flash memory of SSDs accesses data much faster than the NAND flash memory of Embedded Multimedia Card.
Storage Capacity
Embedded Multimedia Cards are on the rise nowadays but still do not provide as much storage as SSDs. eMMC devices only offer up to 256GB of storage. Therefore, it is used in devices with low storage requirements.
SSDs come with a lot of storage these days, with some models even supporting up to 8TB of storage. That’s why it’s used in everything from small-sized to high-performance desktops or data centers.
Cost
eMMC storage is budget-friendly and is therefore used in entry-level and mid-range devices.
SSDs are more expensive than eMMC as they come with higher capacity and are used in premium devices.
Form Factor
The eMMC is integrated directly into the device’s circuitry, which occupies less space. That is why it is mainly used in thin, portable devices with limited space, like mobiles and tablets.
The SSD is used as a separate removable drive. These come in different sizes. Some come in small and large sizes. These come in standard 2.5-inch and M.2 for ultrabooks.
Power consumption
eMMC consumes less power than SSD because it handles light computing tasks that do not require much power. That is why it is suitable for equipment for which cost and power efficiency are important.
SSDs consume more power than eMMCs. SSDs use more complex circuitry to achieve higher performance.
Also Read: Best SSD Laptops
eMMC vs HDDs

| Aspect | eMMC(Embedded Multimedia Card) | HDD(Hard Disk Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Integrated flash | Magnetic disk |
| Form Factor | Compact | Bulky |
| Dimensions | Petite | Spacious |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Read speed | Faster | Slower |
| Write Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Durability | More durable | Less durable |
| Reliability | Solid-state, no moving parts | Mechanical parts may fail |
| Power Consumption | Lower | Higher |
| Noise Level | Silent | Audible mechanical noise |
| Cost | More expensive per GB | Less expensive per GB |
How eMMC Works
1. Writing data to eMMC
Initialization
When an electronic device is turned on or when the storage is initialized, the embedded system firmware or bootloader is activated as part of the device boot-up process.
The device’s SoC or CPU communicates with the eMMC through the storage interface to indicate that both the device and the storage are ready to exchange data.
The device’s firmware or operating system then configures the eMMC by setting various operating modes and parameters. Embedded Multimedia Card storage consists of a memory map that defines how data is organized and stored.
During initialization, the device’s firmware ensures that this memory map is configured correctly, allowing the operating system to interact with the storage effectively. Once the initialization process is complete, the eMMC enters the ready state.
File System Interaction
During File System Interaction, the operating system and the file system manage how data is organized and stored. The operating system interacts with the eMMC through a storage driver to write data.
Controller Handling
The controller of the eMMC manages the process after receiving the data to be written. After identifying the block in which the data is written, it writes new data in the flash memory cells.
Wear Leveling
Wear leveling distributes data evenly across memory cells during write and erase cycles.
Error Checking and Correction
Before data is written, error checking and correction mechanisms check that the data is correct. If there are any errors in the data, the controller corrects them before writing the data to the flash memory.
2. Reading data from eMMC
Data Request
When the device needs to access its stored data, it sends a request to the eMMC.
Controller Handling
When data is requested from the flash memory cells, the eMMC controller retrieves the requested data from the flash memory cells and sends it to the device’s processor.
Transfer to Device
Once correctly checked, the data is transferred to the device’s processor for use by the operating system or application.
Applications of eMMC
Smartphones and tablets
Embedded Multimedia Card is used in smartphones and tablets; it is its standard storage. Such devices have very little physical space. Hence, eMMC is used in it due to its compact form factor.
Laptops and Ultrabooks
Light, thin laptops and ultrabooks have very little physical space and require energy efficiency, so they use eMMC for storage, which consumes very little power and is integrated into the device’s motherboard.
Also Read: Best Cheap Laptops
Digital cameras
eMMCs are used to store photos and videos in digital cameras and webcams that are much smaller due to their compact form factor. The small size of Embedded Multimedia Cards is an advantage in compact camera designs.
Smart TVs and Set-Top Boxes
eMMC is used in smart TVs and set-top boxes to store apps, firmware, and other data that runs the entertainment devices smoothly.
Automotive Infotainment Systems
Automotive infotainment systems are subject to a lot of shock and vibration and are not stable. eMMC is used to store maps, multimedia content, and other data due to its resistance to shock and vibration.
Industrial and Automation Equipment
Industrial systems require embedded storage as it is automated, controlled, and not static. Hence, eMMC is integrated into it so that it can easily withstand shocks and vibrations.
Medical Devices
Embedded Multimedia Card is used in medical devices such as diagnostic devices and patient monitoring systems because these areas do not require much storage, and eMMC provides reliable storage for critical data.
Networking Devices
eMMC is often used in networking equipment such as routers, switches, and network-attached storage (NAS) systems to store firmware, configuration settings, and logs.
Home Appliances
eMMCs are used in home appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, and ovens as smart home appliances store software, user preferences, and operational data.
Wearable Devices
eMMC is used in wearable devices like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and health monitors because these devices are very small. Hence, eMMC is used in these devices due to their compact form factor.
Advantages of eMMC
Cost-effectiveness
The eMMC is integrated into the device’s circuit, so there is no need to make it separately. Its integrated design provides a balance between performance and cost.
Compact Size
eMMC’s compact design makes it suitable for space-constrained devices such as smartphones, tablets, ultrabooks, and thin and light devices.
Energy efficiency
eMMC consumes less power, which is why it is used in portable devices like smartphones and tablets, where battery life is more important than performance.
Reliability
eMMC has no separate parts, making it more robust and resistant to mechanical failures than traditional hard disk drives (HDDs). That is why devices using eMMC have higher reliability.
Versatility
Due to its versatility, eMMC finds application in various devices such as smartphones, tablets, digital cameras, industrial control systems, and more. Its adaptability to various applications makes it widely used in most devices.
Disadvantages of eMMC
Limited Performance
Its performance is very slow in intensive data processing. Compared to SSDs, it has limited read and write speeds, which affects the overall performance of the devices.
Limited Storage Capacity
The maximum storage capacity of eMMC is 256 GB, which is much less than other storage options like traditional HDD or larger SSD, as some devices nowadays support SSD storage up to 8TB. This is not good for devices that require large amounts of data storage.
Fixed Configuration
In eMMC devices, the memory and controller are integrated into a single package. Due to this, it cannot be increased later. This lack of modularity limits the flexibility to customize storage solutions based on specific needs.
Limited Lifespan
Wear-leveling algorithms help evenly distribute write and erase cycles despite eMMC having a limited number of program/erase (P/E) cycles compared to more advanced NAND flash solutions, resulting in higher write Scenarios that may affect the lifetime of storage.
Data Recovery Challenges
Data recovery from eMMC can be challenging if data corruption or failure occurs. This is because eMMC is integrated into the circuit.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Cost-effectiveness | Limited Performance |
| Compact Size | Limited Storage Capacity |
| Energy Efficiency | Fixed Configuration |
| Reliability | Limited Lifespan |
| Versatility | Data Recovery Challenges |
Final Word
Its unique features, wear leveling, error correction, and secure boot set it apart from other storage solutions in terms of versatility and reliability.
The eMMC’s compact design is great for small, thin, and light laptops. Its performance and storage capacity may not be as high as that of an SSD, but it is good for a device that is short on physical space and where battery life is more important than performance.
It is great for thin laptops, mobile phones, and tablets as it is energy efficient, resulting in good battery life for all these devices. Apart from this, it is budget-friendly.




