Day by day Cybercriminals are getting smarter, and their attacks are becoming more dangerous. You might receive an email saying your Microsoft or google account has been locked due to “suspicious activity.”
Most people open the mail and click on the link, thinking their password can be corrected. However, the password is not actually corrected. Instead, after clicking the link, the hacker gains access to all your emails, and your device like laptop, pc, smartphone, tablet, etc also gets hacked. Within a minute, all your files get locked, and they steal your bank account details, personal photos, videos, and more.
This technique is not only used by companies but also by individuals like you and me.
Nowadays, hackers are waiting for an opportunity to scam what you believe is completely real. In such times, it can be difficult to differentiate between a fraud and a legitimate message.
But don’t worry—the good news is that with a little knowledge, you can protect your laptop, PC, or smartphone from such threats.
In this article, we will discuss the 10 best ways to secure your PC, laptop, and passwords properly. We will also provide complete information on how to avoid such scams and protect your personal data.
PC Security in 2025: How to Defend Against Hackers
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Why Strong Passwords Matter
Using weak or repeated passwords is one of the easiest ways to get hacked. In 2025, cybercriminals will use automated tools to test stolen passwords on multiple sites. If your online site’s password is the same as your email or bank account, you’re making it easy for them to break in.

How to Create a Strong Password
Step 1: Go for Length Over Complexity
A password with at least 12 characters is much harder to crack. Something like Apple*Tiger$Run42 is far more secure than P@ssw0rd! because longer passwords have more randomness, making them difficult to guess for hackers.
Step 2: Avoid Common and Personal Information
Hackers can guess passwords based on details like pet names, birthdays, or commonly used words. Instead, use a random but memorable phrase, such as CoffeeMug#BangsAtMidnight.
Step 3: Use a Unique Password for Every Account
If one of your accounts is compromised, having different passwords for each online sites ensures that hackers can’t access everything at once.
The Importance of a Password Manager
Remembering and managing multiple passwords can be stressful, but a password manager makes it easy. Free tools like Microsoft, Google, Bitwarden or premium options like 1Password help by:
- Generating strong, unique passwords for every account
- Securely storing and auto filling login details
- Encrypting your passwords and syncing them across devices
For added security, enable biometric authentication (fingerprint or face ID) on your password manager. Even if your phone is stolen, your passwords remain safe.
What Happens If You Forget Your Password?
We’ve all been frustrated by having to reset passwords. A password manager takes away that hassle by offering:
- Recovery Phrases – A master key to reset your vault if needed
- Emergency Contacts – A trusted person who can help regain access if you’re locked out

2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): 2 Factor Authentication (2FA)
Passwords alone are not enough to protect your accounts. Hackers can steal or guess them, but Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) like 2 Factor Authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security. Even if someone gets your password, they won’t be able to log in without a second step of verification.
MFA works by requiring:
- Something You Know – Your password
- Something You Have – A code from your phone or a security key
- Something You Are – Fingerprint or face recognition
How to Turn On MFA
- Gmail: Go to myaccount.google.com > Security > 2-Step Verification. Use an authenticator app instead of SMS for better security.
- Microsoft: Visit account.microsoft.com > Security > Advanced Security Options > Enable Two-Step Verification.
- Social Media: Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter (X) have MFA options under “Settings and Privacy.”
Avoid SMS for MFA
Hackers can steal your phone number through SIM-swapping attacks. Instead, use Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, or a hardware key like YubiKey for better security.
What If You Lose Access to MFA?
- Backup Codes: Save them securely in a password manager.
- Trusted Devices: Set up a backup login method on a device you trust.
- Recovery Contacts: Add a trusted person’s email or phone number for emergencies.
According to Microsoft, accounts with MFA are 99.9% less likely to be hacked.
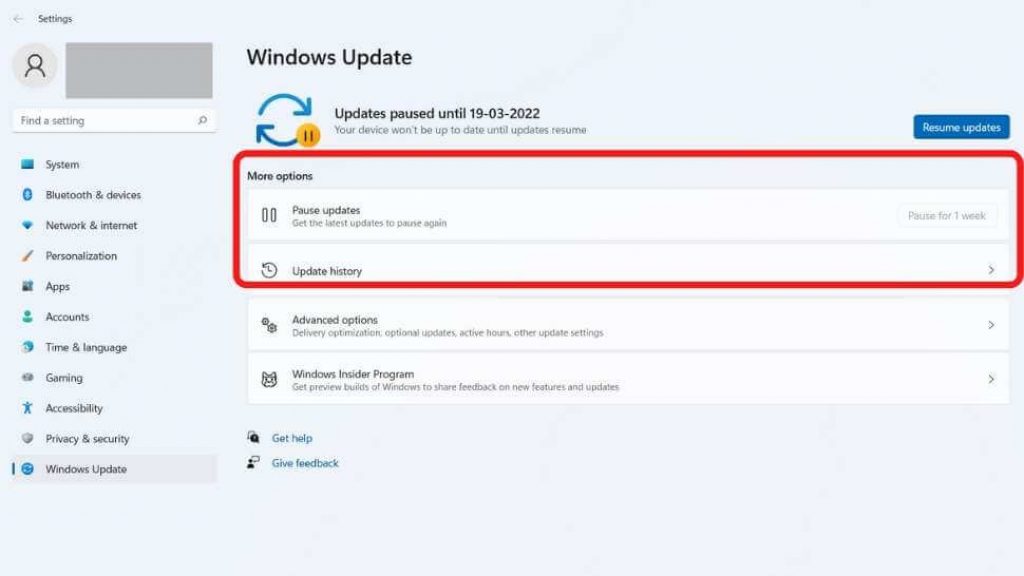
3. Keep Your Software and Operating System Updated
Hackers target outdated software because it has security flaws. If you don’t update your apps, browser, or operating system, your device becomes vulnerable to malware, data breaches, and cyberattacks.
Why Software Updates Matter in 2025
- Fix Security Vulnerabilities: Updates patch newly discovered flaws, preventing hackers from breaking in.
- Improve Performance: Bug fixes make your apps run faster and more smoothly.
- Boost Security: Many updates add extra layers of protection to keep your data safe.
How to Keep Everything Updated
Windows & macOS: Turn on automatic updates in system settings.
Windows 10/11:
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- Enable Automatically download and install updates.
- Under Advanced Options, ensure “Receive updates for other Microsoft products” is turned on.
macOS:
- Open System Preferences > Software Update.
- Select Automatically keep my Mac up to date.
- Click the ⚙️ icon to enable updates for App Store apps and system files.
Browsers (Chrome, Edge, Firefox): Enable auto-updates to guard against phishing and malware.
- Google Chrome: Click Menu (⋮) > Help > About Google Chrome, and it will update automatically.
- Microsoft Edge: Go to Menu (⋮) > Help & Feedback > About Microsoft Edge to check for updates.
- Firefox: Click Menu (≡) > Help > About Firefox, and it will update itself.
Applications: Always update apps, especially those for banking, communication, or storing personal data.
- Windows/Mac: Open the app store (Microsoft Store/App Store) and update your apps.
- Android/iPhone: Go to Google Play Store/App Store, check for updates, and install them.
For additional security insights, visit the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
How Outdated Software Invites Hackers
Ignoring software updates is like leaving your front door unlocked—it’s an open invitation for cybercriminals. In 2025, hackers use automated tools to scan for outdated systems. A single unpatched app can serve as a gateway for ransomware, spyware, or cryptojacking malware.
Real-World Example:
In early 2024, a zero-day exploit in a popular PDF reader Adobe remained undetected for weeks, allowing hackers to encrypt thousands of systems and demand Bitcoin ransoms. Those who had enabled automatic updates remained secure.
The Rising Threat in 2025
- Zero-Day Exploits: Hackers identify security flaws before developers do. Prompt updates often contain patches for these vulnerabilities.
- AI-Driven Attacks: Cybercriminals use artificial intelligence to scan millions of devices for outdated software. Running an old version of Zoom or an unpatched browser makes you an easy target.
- Regulatory Compliance: Laws like GDPR require businesses and individuals to maintain updated systems. Neglecting updates can lead to hefty fines.
Don’t Forget Third-Party Apps
Your operating system isn’t the only target—applications like Adobe Reader, Zoom, and even games can introduce security risks.
How to Stay Protected:
- Use tools like Patch My PC (Windows) or MacUpdater (macOS) to check for outdated software.
- Uninstall apps you no longer use. That old version of QuickTime? Delete it.
Case Study:
In 2023, hackers exploited a vulnerability in VLC Media Player to distribute malware. Users who updated their software remained unaffected.
Myth: “Updates Slow Down My PC!”
Many believe that updates reduce performance, but modern updates are optimized for efficiency. If your PC feels sluggish after an update, it’s likely due to background processes completing the installation—simply restart your device.
Stat Alert:
57% of users who disable updates experience malware infections within six months (Norton Report, 2024).
The Cost of Ignoring Updates
- Financial Loss: Identity theft costs individuals an average of $12,000 (FTC, 2024).
- Lost Productivity: Reformatting a hacked PC can take 8–12 hours.
- Reputation Damage: A compromised email account sending phishing links to contacts can harm your credibility.
Your Action Plan
✔ Audit Your Software: List installed apps and check for updates.
✔ Enable Auto-Updates: Keep browsers, office suites, and gaming platforms updated.
✔ Delete Abandoned Apps: If you haven’t used an app in six months, uninstall it.
Staying updated is your first line of defense against cyber threats—don’t ignore it.

4. Install a Trusted Antivirus to Protect Your PC
Cyber threats in 2025 are more than just viruses—they include ransomware that locks your files, spyware that tracks your activity, and cryptojackers that secretly use your computer for mining cryptocurrency. Antivirus software acts as a security guard, blocking these threats before they can harm your system.
Free vs. Paid Antivirus: Which One is Better?
| Feature | Free Antivirus | Paid Antivirus |
| Real-Time Scanning | Basic | Advanced & AI-driven |
| Phishing Protection | Limited | Full browser & email security |
| Ransomware Rollback | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| VPN & Dark Web Monitoring | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Customer Support | Limited (forums) | 24/7 live chat |
While free antivirus offers basic protection, paid versions provide stronger security against evolving cyber threats.
Best Antivirus Picks for 2025
- Bitdefender Total Security – Uses AI to detect new threats, great for families (covers multiple devices).
- Norton 360 Deluxe – Includes a VPN, parental controls, and cloud backup.
- Malwarebytes Premium – Excellent for removing stubborn adware and unwanted programs.
Also Read: 15 Best Free Antivirus for Windows 11 in 2025
Tip: Avoid fake “PC boosters” and “registry cleaners” pretending to be antivirus tools. Stick to well-known brands.
How to Install and Set Up Your Antivirus
- Remove Old Antivirus Software – Uninstall previous versions to prevent conflicts.
- Windows: Go to Settings > Apps > Uninstall.
- macOS: Drag the old antivirus app to Trash.
- Download from the Official Website – Get the software directly from trusted sources like bitdefender.com to avoid malware-infected copies.
- Run a Full System Scan – This can take up to 2 hours. Use the time to organize files and free up storage.
- Enable Auto-Updates and Real-Time Protection – For example, in Bitdefender:
- Open the app → Protection → Turn on Advanced Threat Defense.
Schedule Weekly Scans for Extra Safety
Set your antivirus to scan your system once a week, preferably when you’re not using your PC (e.g., Sunday at 3 AM). AI-powered antivirus tools can even detect unusual behavior, like mass downloads in the middle of the night, and alert you.
When Antivirus Isn’t Enough
Even with strong protection, you should stay cautious. Avoid:
- Clicking “Allow” on suspicious pop-ups.
- Downloading software from unknown websites.
- Entering personal details on untrusted sites.
A combination of good antivirus software and smart online habits will keep your PC safe in 2025.
5. Set Up a Firewall to Secure Your Network
A firewall acts like a security guard for your device, monitoring all incoming and outgoing data. In 2025, with smart homes and IoT devices everywhere, having a properly configured firewall is more important than ever.
Types of Firewalls
- Software Firewalls – Built into your operating system (e.g., Windows Defender Firewall).
- Hardware Firewalls – Found in routers (e.g., pfSense for advanced users).
How to Enable Windows Defender Firewall
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Windows Defender Firewall.
- Turn it on for both private and public networks.
- Customize settings:
- Block incoming connections for untrusted apps.
- Allow exceptions for essential tools like video conferencing apps.
Pro Tip: Enable Stealth Mode (in advanced settings) to prevent hackers from detecting your device.
Are Third-Party Firewalls Necessary?
Some tools, like GlassWire (Windows/macOS), provide extra features such as real-time network monitoring.
Example: A user discovered their smart thermostat was secretly sending data to an unknown server in Belarus. With GlassWire, they blocked the connection immediately.
Firewall Myths Debunked
???? “Antivirus alone is enough.” – Firewalls and antivirus work together for complete protection.
???? “Firewalls slow down my internet.” – The impact is minimal unless you’re a competitive gamer.
Firewall Security Checklist
✅ Enable your built-in firewall.
✅ Block unknown inbound connections by default.
✅ Regularly review app permissions.
A well-configured firewall adds an extra layer of security, keeping your devices and data safe.

7. Back Up Your Data: The 3-2-1 Rule
Your data is valuable—don’t risk losing it. Follow the 3-2-1 backup rule to stay protected:
- 3 Copies – Keep the original and two backups.
- 2 Formats – Use a mix of cloud storage (Google Drive) and physical storage (external SSD).
- 1 Offsite Copy – Store a backup in a different location to protect against theft or disasters.
???? Example: A photographer stored all wedding photos on a single hard drive. When it failed, they lost $10,000 worth of work. A backup could have saved them.
Best Cloud Backup Options
| Service | Best For | Free Tier | Price (2025) |
| Backblaze | Unlimited backups | 15-day trial | $7/month |
| Google Drive | Collaboration & sharing | 15GB | $2.99/month (200GB) |
| iDrive | Multi-device backups | 10GB | $79.50/year (5TB) |
✅ Pro Tip: Encrypt your backups before uploading using tools like Cryptomator for extra security.
Automate Backups: Set It & Forget It
For Windows:
- Connect an external drive.
- Go to Settings > Update & Security > Backup.
- Click Add a Drive and select your SSD.
For macOS:
- Open System Preferences > Time Machine.
- Select a backup disk and enable encryption.
???? Schedule Weekly Backups – Set them for 2 AM so they run without interruptions.
Test Your Backups: Avoid Surprises
Once a month, restore a file from your backup to ensure everything works.

7. Stay Safe from Phishing Attacks
Phishing isn’t just about spam emails anymore. In 2025, hackers use AI to clone voices, fake video calls, and craft emails so realistic that even tech-savvy people fall for them. Imagine getting a call from “your boss” asking for an urgent wire transfer—except it’s not really them. Scary, right? But don’t worry, if you know what to look for, you can outsmart these scams.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a cyberattack where scammers try to trick you into giving up sensitive information—like passwords, banking details, or personal data—by pretending to be someone trustworthy.
Real-World Example: The Fake CEO Scam
In 2024, a CEO received a Slack message from a “colleague” asking them to review an urgent contract. The message contained a link that looked legitimate, but when clicked, it installed spyware. The hackers used it to steal confidential company data.
???? The red flag? The colleague’s email address was slightly misspelled: john.doe@companyy.com instead of john.doe@company.com.
How Phishing Scams Work
Phishing attacks rely on three main tactics:
1️⃣ The Bait – How Scammers Lure You In
Attackers create messages that trigger emotions like urgency, fear, or curiosity. Common tactics include:
- Fake Urgent Warnings:
- “Your PayPal account will be suspended in 24 hours unless you verify your details!”
- “We noticed an unusual login attempt from Russia. Secure your account now!”
- Too-Good-To-Be-True Offers:
- “Congratulations! You won a free iPhone 15! Click here to claim your prize.”
- “Get a 90% discount on your next Amazon order. Limited time only!”
- Social Engineering Tricks:
- Attackers impersonate a boss, coworker, or even a friend:
- “Hey, can you send me the company’s bank details? I need to process a payment.”
- “Mom, I lost my phone! Send money to this number urgently!” (A common scam targeting parents.)
- Attackers impersonate a boss, coworker, or even a friend:
2️⃣ The Hook – How They Steal Your Information
Once you take the bait, the scammers try to steal your data through:
- Malicious Links:
- Fake login pages designed to look like Google, Microsoft, or PayPal.
- Hover over the link before clicking—does it lead to amaz0n.com instead of amazon.com?
- Fake Attachments:
- Emails with attachments labeled as “invoices,” “job offers,” or “important documents.”
- Clicking on them installs malware that steals passwords or locks your files (ransomware).
- Voice or Video Deepfakes:
- AI-generated calls or video messages impersonating your CEO, asking for financial transactions.
3️⃣ The Payoff – What Happens If You Fall for It?
If a phishing attack is successful, you might:
- Have your email and social media hacked.
- Lose money from your bank account.
- Have your company data stolen.
- Get locked out of your own system due to ransomware.
How to Recognize a Phishing Email or Message
???? Use this checklist to avoid getting scammed:
✅ Check the Sender’s Email Carefully
- Does the email address look slightly off? (e.g., support@paypai.com instead of support@paypal.com).
- If an email is from someone you know but seems strange, call or message them separately to verify.
✅ Hover Over Links Before Clicking
- A real bank will send you to bankofamerica.com, not b4nk-america-login.com.
✅ Watch for Poor Grammar and Formatting
- Many phishing emails contain weird phrasing or typos.
✅ Be Skeptical of Urgent Requests
- Scammers want you to act before you think. Pause and verify first!
✅ Never Share Sensitive Information Over Email or Messages
- Banks, PayPal, and Google will never ask for your password via email.
✅ Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Even if a hacker steals your password, they can’t access your account without your MFA code.
✅ Report Suspicious Emails
- Forward phishing emails to your IT team or report them to reportphishing@apwg.org.
What to Do If You Clicked a Phishing Link
We are generally frustrated, Uh-oh! You clicked on a bad link. Now what?
Step 1: Disconnect from the Internet
- Turn off Wi-Fi or unplug your Ethernet cable to stop data from being sent.
Step 2: Run a Full Malware Scan
- Use antivirus software like Windows Defender, Malwarebytes, or Bitdefender to check for threats.
Step 3: Change Your Passwords Immediately
- If you entered your login details on a fake site, change that password ASAP.
- Update important passwords (email, banking, social media).
Step 4: Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- This adds extra protection even if your password gets stolen.
Step 5: Contact Your Bank If You Gave Away Financial Info
- Freeze your card or account if needed.
Step 6: Report the Phishing Attempt
- Tell your IT department, employer, or bank.
- Forward phishing emails to reportphishing@apwg.org to help stop scammers.

8. Secure Your Wi-Fi Network
Why Your Router is the Weakest Link
Your Wi-Fi router is the gateway to every device in your home—smart TVs, baby monitors, even your fridge. In 2025, hackers exploit outdated routers to launch botnet attacks or spy on unencrypted traffic.
Horror Story:
A family’s Nest security cameras were hacked because their router used the default password “admin.” The intruders livestreamed their home on the dark web.
Step-by-Step: Locking Down Your Wi-Fi
Step 1: Change Default Router Credentials
- Log into your router’s admin panel (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Replace the default username/password (e.g., “admin/admin”) with a strong passphrase.
Step 2: Enable WPA3 Encryption
- WPA3 is the latest standard. Avoid WEP or WPA2—they’re outdated and crackable.
- Navigate to Wireless Settings > Security > WPA3-Personal.
Step 3: Hide Your Network SSID
- Prevent your Wi-Fi name from broadcasting publicly. Go to Wireless Settings > Hide SSID.
Step 4: Set Up a Guest Network
- Isolate visitors from your main devices. Limit guest access to specific hours.
Step 5: Update Router Firmware
- Manufacturers patch vulnerabilities regularly. Check for updates monthly.
Public Wi-Fi: How to Stay Safe
Coffee shop Wi-Fi is a hacker’s playground. Protect yourself:
- Use a VPN: Tools like NordVPN or ExpressVPN encrypt your traffic.
- Avoid Sensitive Tasks: Never bank or shop on public networks.
- Forget the Network: Ensure your device doesn’t auto-reconnect.

9. Manage User Access and Permissions
The Principle of Least Privilege: Why Your Kids Shouldn’t Have Admin Rights
Giving everyone admin access is like handing out house keys to strangers. Restrict accounts to only what’s necessary:
- Administrator Accounts: For installing software or changing system settings.
- Standard Accounts: For daily tasks like browsing and email.
Case Study:
A teenager downloaded a “free” game mod that secretly installed ransomware. Because they used an admin account, the malware encrypted the entire family’s photos and documents.
How to Set Up User Accounts
Windows:
- Go to Settings > Accounts > Family & Other Users.
- Click Add Account > Standard User.
- Require a password for installations.
macOS:
- Open System Preferences > Users & Groups.
- Click the + icon and select Standard under New Account.
Pro Tip: Use parental control tools like Qustodio to block risky websites for kids.

10. Encrypt Sensitive Data
Encryption 101: Turning Your Data into a Digital Vault
Encryption scrambles your files into unreadable code. Even if hackers steal your laptop, they can’t access your data without the decryption key.
Windows (BitLocker):
- Type “BitLocker” in the Start menu and select Turn on BitLocker.
- Choose to save your recovery key to a USB or Microsoft account.
- Encrypt the entire drive (recommended for maximum security).
macOS (FileVault):
- Go to System Preferences > Security & Privacy > FileVault.
- Click the lock icon, enter your password, and select Turn On FileVault.
- Store the recovery key in iCloud or print it.
Encrypting Individual Files
Use VeraCrypt to create password-protected containers for sensitive documents:
- Download VeraCrypt and create a “volume.”
- Mount the volume as a virtual drive.
- Drag files into it—they’ll encrypt automatically.
Pro Tip: Name encrypted containers something boring like “Tax_Forms_2024” to avoid suspicion.
FAQs
Q1: How often should I change my Wi-Fi password?
It is better to change Wi-Fi password for every 6–12 months, or immediately if you suspect a breach.
Q2: Can phishing attacks target laptop, pc, and mobile devices?
Yes! All of these devices can be hacked, so avoid clicking on links in unsolicited messages or social media DMs.
Q3: Is Windows Defender enough for antivirus?
For basic use, yes. Pair it with Malwarebytes for occasional scans.
Q4: What’s the safest way to store recovery keys?
Use a password manager or a fireproof safe—not sticky notes on your desk.
Q5: Can I encrypt external hard drives?
Absolutely. BitLocker (Windows) and Disk Utility (macOS) both support external drive encryption.