Boosting the CPU’s Speed for high performance is nothing new in computer engineering. This technology has proved very useful in some situations and has powerfully met the requirements of high-performance demanding users.
Boosting the CPU is the technology that makes the CPU work faster and smoother when there is a demand for more processing power. Increasing technology makes the system optimized and valuable for users who run high-end tasks like extreme gaming, complex editing programs, etc.
Thermal Velocity boost is a built-in capability found in Intel’s CPUs for quite a long time. This technology is further enhanced by recently adding a new Intel TVB feature.
Intel Thermal velocity boost is the CPU boosting feature that increases the processor’s Speed within the CPU’s tolerable temperature range. If there is a significant load on the system, a TVB automatically activates and makes the CPU run faster, thus enhancing its performance.
Because of the latest technology and innovation, The thermal velocity boost feature is unique among all CPU generations, and only 10th,11th, 12th, and 13th-generation Intel processors support this feature.
How does a TVB enhance the efficiency of a CPU’s performance?
Thermal velocity boost uses a similar mechanism as the turbo boost, but it makes the compatible CPUs even more efficient in performance. A TVB enhances the processor’s Speed faster than the previous turbo boost.
Thermal Speed is an energy-efficient and adaptable technology that allows the CPU to run at the base frequency when the workload is minimal and at a higher frequency.
When the demanding tasks run, the system can perform at a higher rate when the heavy load is heavy. Aspects are more efficient to throw at it.
It also makes the system run smoother instead of slowing down. TVB(thermal velocity boost) has two boost modes:
- Single-core boost: This mode boosts the Speed of only one CPU core and makes it run faster than the base frequency.
- The all-core boost feature enhances the clock frequency of all CPU cores simultaneously. It results in a significant performance boost, which results in additional pressure on the processor and may exceed the CPU’s tolerable range, making it risky and challenging but useful.
Other boost modes that were previously used
Turbo boost modes 2.0 and 3.0 were the major boosting features available long before introducing and releasing a thermal velocity boost feature. These modes enhance the clock speed of either one or many cores of a multiple-core processor.
So, this boosting feature emphasizes one or more cores and makes them run at their extreme limits by automatically identifying the size of the load on the system. But this boosting feature only works if it meets certain requirements. The CPU temperature must stay below a specific point known as the threshold temperature, and the system must use the optimum power and current.
The Turbo Boost 3.0 is more efficient and enhanced than the 2.0 version, intensifying the clock speed of two CPU cores. The performance of single-core is significantly increased as compared to the base frequency.
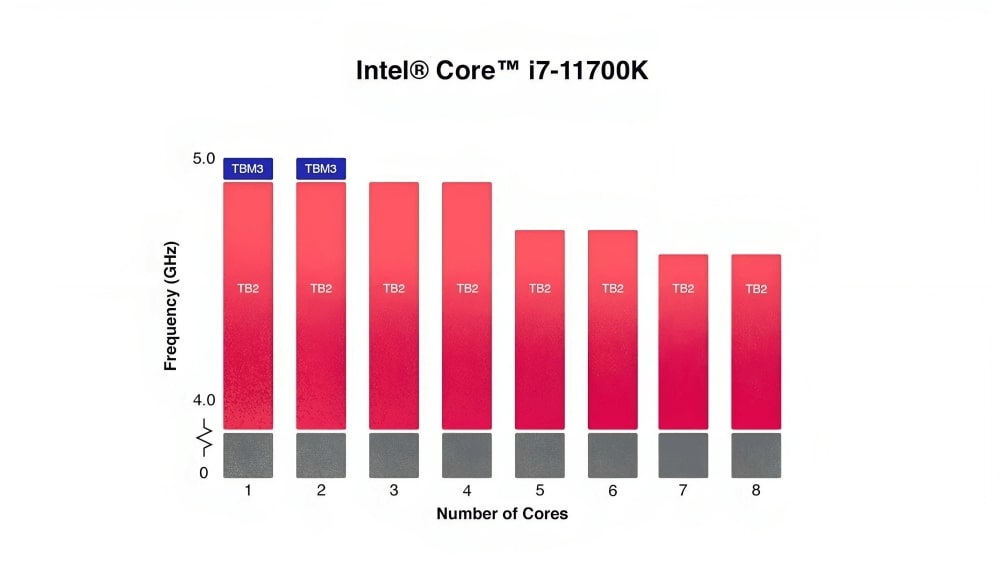
Intel Thermal Velocity Boost vs. Turbo Boost.
The boosting feature available in Intel CPUs before the TVB technology was a turbo boost. It was compatible with relatively lower generation CPUs like Intel core i3, i5, i7, and Xeon series, unlike TVB, the latest line in boosting technology.
This is the most common boosting feature found in Intel CPUs ever since its release in 2008. The turbo boost can increase the CPU’s base clock speed by up to 1 GHz step by step in small increments, providing additional processing power for handling demanding tasks and programs.
This turbo boost doesn’t work each time the processor is running; instead, it works depending on the workload provided to the system.
The turbo boost technology includes running a high graphics game, video editing for your professional business, making a 3D model using heavy Software, and many more.
Hardware compatibilities for intel thermal velocity boost
It works on various Intel processors, making them run faster for tasks, especially single-threaded ones. But it stops if the CPU gets too hot. To use TVB, you also need a compatible motherboard and BIOS.
TVB is available on the following Intel processors:
- 12th Generation Core i9, i7, i5, i3, and Celeron processors
- 11th Generation Core i9, i7, i5, i3, and Pentium processors
- 10th Generation Core i9 desktop processors
- 10th Generation Core i9, i7, and i5 mobile processors
- Intel Xeon W-1200 lineup
In general, typical consumers and low-end programs are familiar with traditional, relatively standard boosting technology, including turbo boost, which is present in almost all lower-generation CPUs except for a few.
Is there any need for me to have an Intel thermal velocity boost?
Suppose you’re a serious user and often have to compromise on the performance of your CPU to run high-end programs and Software. In that case, the CPU’s Intel thermal velocity boost will benefit you.
But if you are an average user who doesn’t have a high workload and complex applications on your system, this may not be your purpose.
How do I use the thermal velocity boost feature on my PC?
This technology has no configuration to enable and work as this is an altogether by-default feature with compatible processors, making the peak frequencies achievable.
To benefit from the Thermal Velocity Boost feature on your PC, ensure the following:
- You have an Intel processor that supports Thermal Velocity Boost.
- Your motherboard is compatible with Thermal Velocity Boost.
- Keep your BIOS updated to the latest version.
FAQs
There is no doubt that gamers and enthusiasts will benefit from this technology.
Thermal Velocity Boost will not only enhance your gaming experience but will also make it more realistic.
Game developers also use Thermal Velocity Boost to create realistic video game worlds. This will allow players to immerse themselves even more in games.
Overall, gamers and enthusiasts will benefit greatly from this technology.
Using Thermal Velocity Boost has several advantages:
Faster Performance: It makes your computer work faster, especially for tasks that use just one part of it.
Less Power Use: Your processor won’t need to use as much power to go faster when it’s cool so it can save energy.
Longer Lifespan: Because your processor doesn’t run too hot as often, it can last longer without getting worn out.
The only downside is that it can raise your processor’s temperature. But this isn’t usually a concern if you have effective cooling.
The performance boost from TVB varies depending on your processor model, how well your PC is cooled, and what tasks you’re doing.
But overall, it can give a noticeable speed boost, especially for tasks that use only one part of your computer.
Final Words
By default, the thermal velocity boost feature enables the users to gain maximum output from the processor. It maximizes your system’s performance and doesn’t harm or damage the CPU if it runs at its peak-rated clock speed.
Altering its maximum upper-rated frequency, as done in overclocking, is not possible with Thermal Velocity Boost. While some changes in BIOS settings can disable it, this can be risky and harmful to the CPU, so it is not recommended to attempt to disable it.




