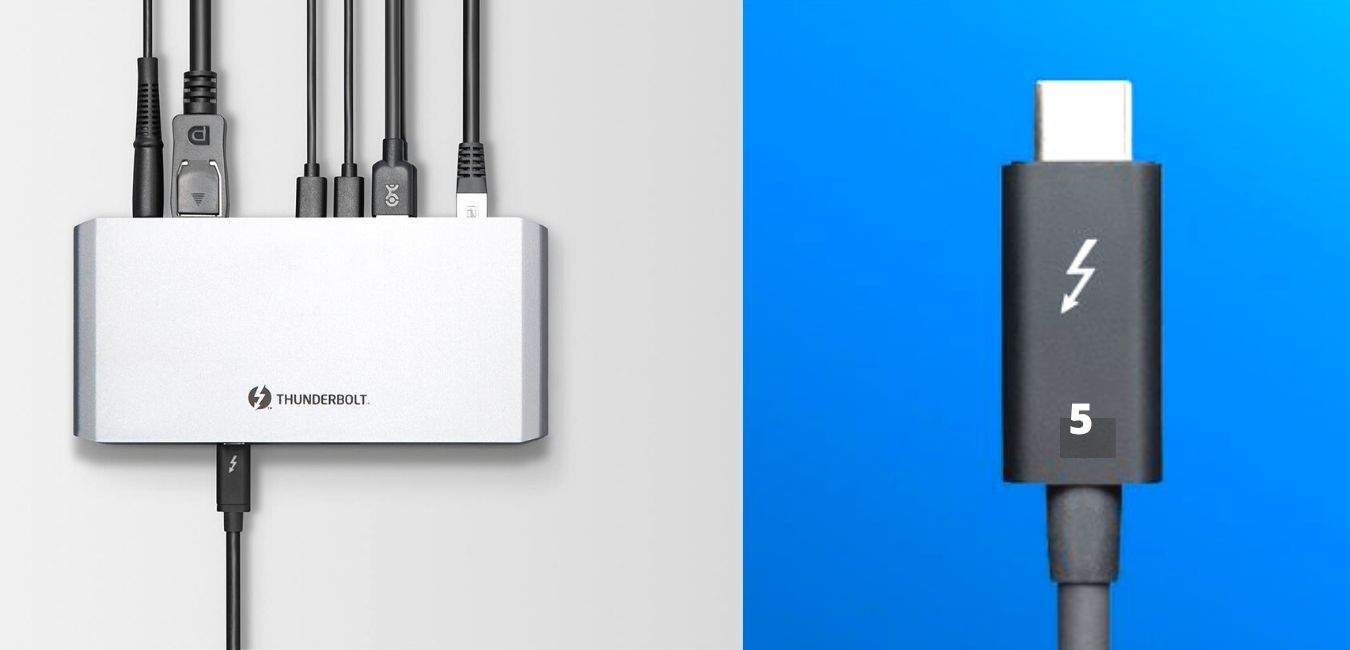
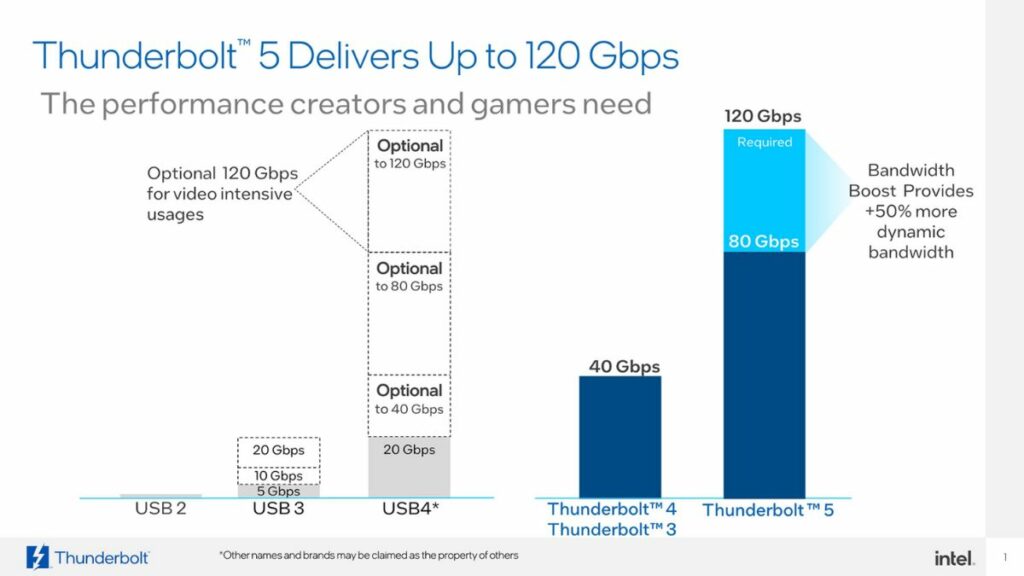
Since Thunderbolt technology has become a trend in the market, as many of the best features will provide high-speed data transfer from a USB Type-C port, Thunderbolt 5 will deliver an impressive 80 gigabits per second (Gbps) bi-directional bandwidth. Additionally, the bandwidth boost will increase up to 120 Gbps.
Thunderbolt 3 and 4 ports are very popular and excellent. For example, you can easily use an external monitor, transfer data with higher bandwidth, charge another device, etc.
Table of Contents
History of Thunderbolt
Apple was the first to adopt Thunderbolt. Before the standard was updated to use the USB-C connector, different ports were integrated into different Macs — which led to all the chaos that followed.
Premium brands Intel and Apple created Thunderbolt technology. Thunderbolt technology has been separated from Apple and established as a separate brand.
When Intel announced Thunderbolt 4, people naturally expected it to increase the 40 Gbps bandwidth provided by its predecessor, but it did not, and Thunderbolt 4 also remained at 40 Gbps.
Thunderbolt 5 Release Date
Intel demonstrated Thunderbolt 5 in October 2022, and its features were announced in September 2023. Intel hasn’t revealed an exact release date for Thunderbolt 5, but the company has assured it will start appearing in upcoming devices in 2024.
As in previous generations, Thunderbolt 5 was integrated into Intel’s processors; this time, it will require a separate chip. It will first be offered in devices geared toward gamers and content creators rather than productivity or workstation computers.
Computers and accessories with Thunderbolt 5 will begin to appear in 2024, and technical details will be shared with device manufacturers to facilitate their preparations.
Notably, a prototype device has already been demonstrated by Intel, and the technology was demonstrated at an event in Israel last year, even before it was officially named “Thunderbolt 5”.
Thunderbolt 5 Speed

Thunderbolt 5 is set to revolutionize connectivity with its powerful speeds of up to 80 Gbps in both directions, which is double the speed of the previous Thunderbolt 4, which was 40 Gbps. This speed is achieved through four data lanes, each supporting 40Gbps.
The adaptability of Thunderbolt 5 shines in the unique configuration, providing an extraordinary 120 Gbps bandwidth for data transmission in one direction, which is three times more bandwidth than existing connectivity options.
Support for the extraordinary 120 Gbps data transmission in one direction comes from the USB 4 version 2.0 spec, which is 5 times faster than Thunderbolt, introduced in 2011.
They are designed to meet the needs of content creators and gamers who require fast data transfers. Its fast speeds will facilitate super-resolution displays, low-latency viewing for immersive gaming, and efficient backup or transfer of massive video and data files. It is also believed to support much higher refresh rates for 4K and 8K monitors, making it a game-changer in display technology.
The Thunderbolt 5 interface will use two virtual pipes to transmit data to one device and two virtual pipes to receive data to another device, each at a speed of 40 Gbps. It can also transfer current by sending up to 240 watts of power, which will be great for current and future laptop battery needs.
Thunderbolt 5 specs and features
Bandwidth Boost
Thunderbolt 5 will have a special feature called “Bandwidth Boost.” It will, therefore, be able to use even more bandwidth, up to 120 Gbps in one direction, for tasks requiring higher speeds, which is three times more than previous Thunderbolt versions.
High Speed
Thunderbolt 5 will be much faster than its predecessors, transferring data at up to 80 Gbps in both directions and a maximum speed of about 120 Gbps in one direction.
Support for High-quality Displays
It can handle three 4K displays simultaneously, so it will be no problem watching videos, playing games, or working on multiple screens. It will also support high refresh rates, up to 540Hz, for super smooth visuals.
More Power Delivery
Thunderbolt 5 will provide more power to the device. It can provide as little as 140 watts of power and can be configured to deliver up to 240 watts for manufacturers. It will be useful for charging powerful laptops and other devices.
Versatile Docking
Thunderbolt 5 will be used for various connecting solutions ranging from monitor stand docks to portable and commercial docks. Intel says that using Thunderbolt 5 for docking will be better than alternatives that compromise data speeds and video quality.
External GPU (eGPU) Support
Thunderbolt 5 will lead to external GPUs, which are expected to provide better performance capabilities and make them more popular for gaming and creative work.
Multiple ports on device
Computers designed with Thunderbolt 5 can have up to four Thunderbolt 5 ports, providing more options for connecting different devices.
Compatibility
There will be a separate chip for Thunderbolt 5, through which the update will run on silicon. Due to this, it can be used in Intel-based devices and computers running on different platforms.
Real-World Uses for Thunderbolt 5
Thunderbolt 5 isn’t just faster on paper — it changes what’s possible for professionals, gamers, and power users. Here’s where the upgrade really makes a difference:
Video Editing and Content Creation
Working with 8K or high-bitrate 4K footage? Thunderbolt 5’s PCIe 4.0 speeds cut file transfer times nearly in half. For example, in Adobe Premiere Pro, rendering a 10-minute 8K clip can be 30–40% faster when using Thunderbolt 5 storage compared to Thunderbolt 3.
Coupled with support for multiple high-refresh 4K or 8K monitors, you can edit, preview, and export without lag. This is perfect for video editors, YouTubers, and creative professionals managing large media files.
Gaming on Multiple High-Refresh Displays
Gamers using external GPUs or multi-monitor setups benefit from smoother visuals. Thunderbolt 5 gaming performance shines here, driving up to three 4K monitors at 144Hz — a huge improvement over Thunderbolt 3’s dual 4K limit. This ensures faster response times, immersive gameplay, and better eSports or simulation performance. In real tests, running triple 4K monitors at 144Hz through TB5 reduced input lag by up to 15% compared to TB3.
Professional 3D and CAD Work
Architects, engineers, and 3D artists often juggle multiple monitors and huge project files. Thunderbolt 5’s increased bandwidth and PCIe 4.0 support speed up rendering, 3D modeling, and large CAD workflows. You can transfer complex project files between devices quickly, keeping work uninterrupted. For example, rendering a large Revit or SolidWorks model can be up to 35% faster when using TB5 vs TB3.
High-Speed Data Backup and Archiving
For those handling terabytes of data — like photographers, filmmakers, or researchers — Thunderbolt 5 drastically reduces backup and archiving times.
Large media libraries, datasets, and project archives can move at 6,700 MB/s, compared to 2,800 MB/s on Thunderbolt 3. This means a 1TB backup can take just under 3 minutes on TB5, versus over 6 minutes on TB3.
Docking and All-in-One Workstations
Thunderbolt 5 supports more devices through a single hub. You can connect multiple monitors, external storage, and networking devices without slowing down transfers.
Ideal for designers, video editors, and remote workers who need clean, high-performance desk setups. A single TB5 dock can replace multiple TB3 docks by providing extra bandwidth for all peripherals.
Charging Power-Hungry Laptops
With up to 240W power delivery, Thunderbolt 5 can charge gaming laptops, mobile workstations, and other high-performance devices via a single cable.
This reduces the need for multiple chargers and keeps desks clutter-free. In practice, charging a 99Wh laptop battery from 0 to 50% can be done in around 30 minutes via TB5.
Multi-User Collaboration
Thunderbolt Networking now reaches 20 Gbps, making PC-to-PC transfers faster than ever. Teams working on large media projects, CAD files, or research data can collaborate seamlessly without waiting for slow transfers. For example, sharing a 200GB project folder between two TB5-enabled systems can take under 2 minutes, compared to about 5 minutes with TB3.
Thunderbolt 5 Cable
Thunderbolt 5 cables will be approximately 2 meters (6.56 feet) long. This cable will be a Thunderbolt 4 branded cable and will be made for Thunderbolt 5 by adding additional features. Fully Thunderbolt 5 branded cables will take a little longer to arrive.
Thunderbolt 5 PAM-3 Technology
Thunderbolt 5 will use PAM-3 technology to work faster and better. The older version used PAM-2 technology, which had an “eye” every time information was sent. But PAM-3 will have two “eyes” every time information is sent, making data transfer faster. This change is part of the USB4 version 2.0 specification.
The special thing about PAM-3 is that it allows Thunderbolt 5 to adjust the speed depending on the task. This will mean that whenever you need very high speeds, you can use a special mode to go even faster, up to 120 Gbps.
If you’re using Thunderbolt 4 or older, Thunderbolt 5 may still work with it. But you will switch to the older technology, PAM-2.
Also Read:
FAQs
Q1. What is Thunderbolt 5?
Intel and Apple developed the Thunderbolt hardware interface under the Thunderbolt brand name. It enables the connection of external peripheral devices to the computer.
Thunderbolt 1 and 2 share the Mini DisplayPort (MDP) connection, while Thunderbolt 3 uses the USB-C connector. It was initially introduced as part of an end-user product on February 24, 2011, and was developed and sold under the name Light Peak.
Thunderbolt combines PCI Express (PCI) and DisplayPort (DP) into two serial signals with DC power, all within a single cable. Depending on the topology of the peripheral device, a single connection can accommodate up to six connectors.
Q2. Why Do AMD Laptops not have a Thunderbolt port?
There are a few reasons why AMD laptops do not come with a Thunderbolt port.
Thunderbolt is designed to achieve high-speed data transfers between devices, including computers and external graphics interfaces. Although AMD has been working on integrating this technology into its laptops, it still requires implementation.
The second reason is that AMD laptop ports are typically set up for audio and video output. Because Thunderbolt isn’t intended for these functions, connecting an external graphics adapter or other devices may result in performance problems.
Thirdly, Thunderbolt is not backwards compatible with USB 3.0, meaning that you need to switch to a newer USB 3.0 port if you want to use an older USB device.
Q3. What’s new in Thunderbolt 5?
However, due to some leaks, some important information has been lost. Intel executive Gregory Bryant posted an early glimpse of Thunderbolt 5 on X (Twitter) and immediately deleted it, claiming that it has 80G PHY technology, twice that of Thunderbolt 4.
The leak clearly shows that this will refer to physical connectors that support connections up to 80 Gbps, a significant improvement over its predecessor, 40 Gbps.
This is not the official information now available, but the rumored information posted on X (Twitter) by intelligence officials. So when it is released, some changes can also be found.
Source: Wikipedia
Final Words
In the fast-changing technological world, Thunderbolt will be able to transfer data faster through USB Type-C port. Thunderbolt 3 and 4 are already well-liked for their many uses, like connecting screens, sending data, and charging devices.
A sneak peek at Thunderbolt 5 reveals that it may feature 80G PHY technology, making it twice as fast as Thunderbolt 4. Although not official yet, it’s a good sign.
We may see Thunderbolt 5 as early as 2024, which will bring faster data transfers and better graphics.