Storage is crucial in computing. When working on a computer, data is accessible as long as the computer is on. Once the computer is turned off, volatile memory, like RAM, loses the data it stores. However, permanent storage devices, such as HDD or SSD, retain data even when the computer is powered off, ensuring its availability between sessions.
Storage is what keeps data even when the computer is turned off so that the data can be accessed anywhere at any time. You can also back up your data in case of system failure or accidental deletion.
Where will you keep the operating system, programs, and applications without storage? Therefore, space is required to keep all this. They store many files such as documents, images, music, videos, etc.
If you have external storage devices like USB drives and portable hard drives, you can transfer data from one location to another.
The storage that came earlier did not have much capacity; hence, there was difficulty in storing large files. To overcome this problem, HDD was brought into the computing field, which comes with a huge storage capacity and stores large files inside it easily.
What is an HDD?
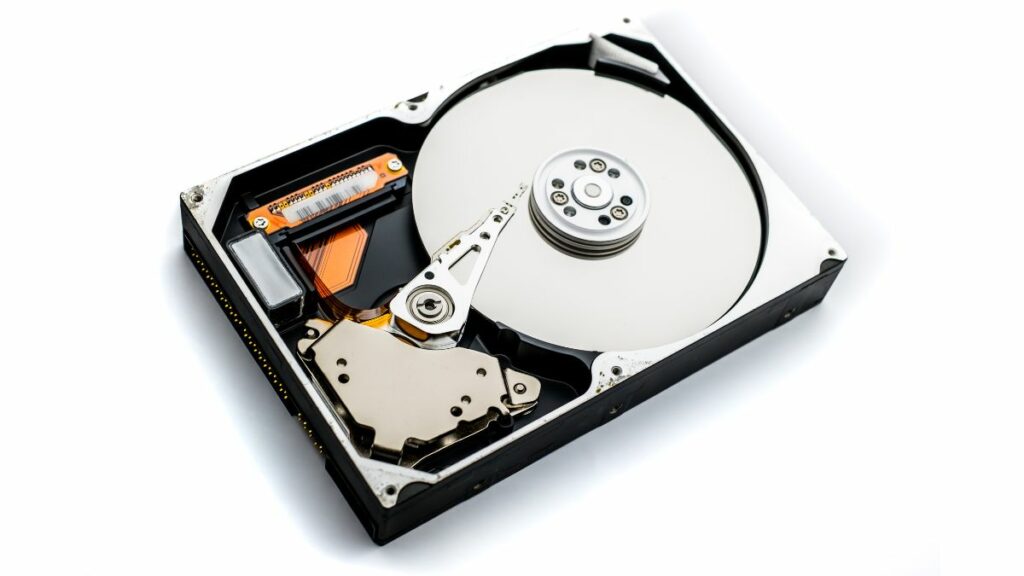

HDD stands for Hard Disk Drive, which is a non-volatile data storage device. It uses magnetic storage to store and retrieve data. HDDs have been used as primary storage for many years. These consist of one or more rotating disks coated with a magnetic material, and data is written and read using a magnetic head mounted above the rotating disk.
Components of an HDD
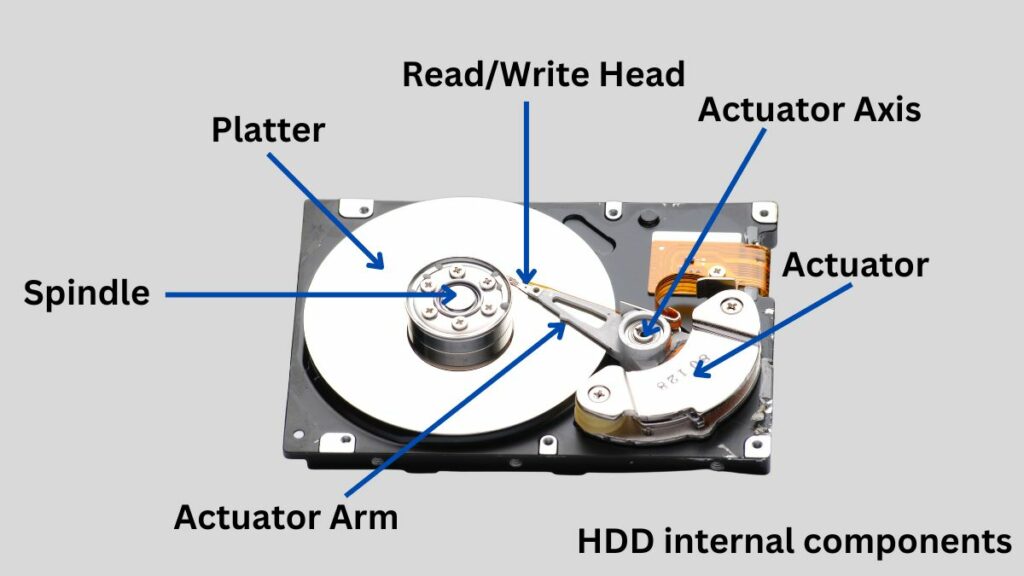
Platters
Platters are circular discs made of aluminum or glass coated with a magnetic material. This disk stores data. These platters are placed one above the other on the same axis and rotate together.
Spindle
A hard disk has a motor called a spindle, which rotates the platters at a constant speed. This rotational speed is fundamental to an HDD’s ability to access and retrieve data efficiently.
Read/Write Heads
Read/write heads are small electromagnetically sensitive devices mounted on the end of an actuator arm whose primary function is to read data from and write data from magnetic plates.
Actuator Arm
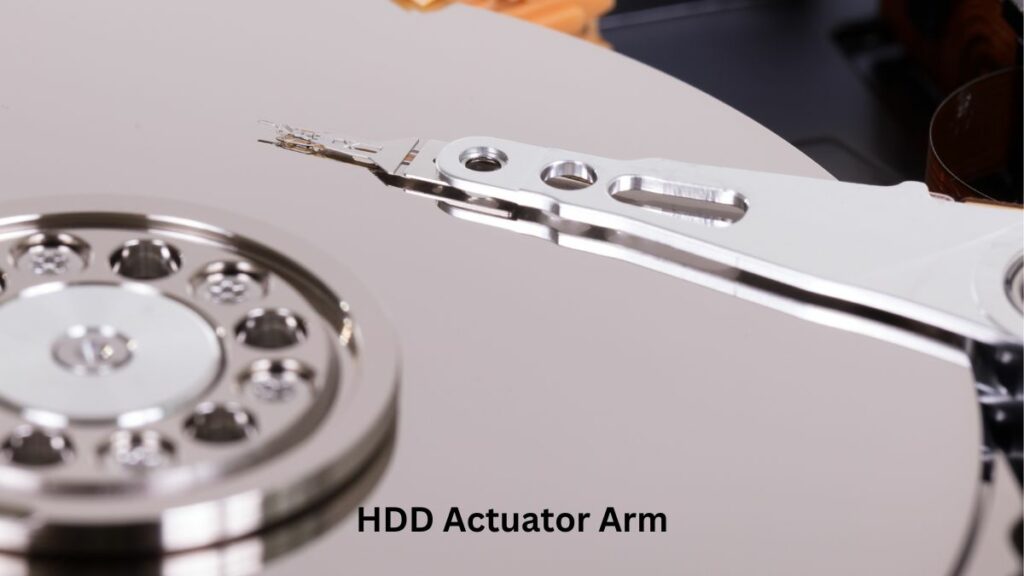

The actuator arm is a mechanical arm inside the HDD that moves the read/write head across the platters. The movement of the actuator arm is controlled by an electromechanical system that precisely adjusts its position based on signals from the drive’s controller.
Controller Board
The controller board, also called the HDD controller or disk controller, is an important electronic component located on the circuit board of an HDD. It manages and coordinates the activities of various components, actuator arms, read/write heads, spindles, and data processing functions, acting as an intelligence hub.
Types of HDDs
There are many types of HDDs, each with advantages and disadvantages. The most common HDDs including-
1. PATA
PATA stands for Parallel Advanced Technology Attachment. This is an older interface that is the most common type. These have much slower data transfer rates and lower capacity and also use wider cables that are more difficult to install. Due to all this difficulty, it was replaced by SATA, which provides faster data transfer and has better capacity than PATA.
2. SATA
SATA stands for Serial Advanced Technology Attachment, which is currently the standard for HDD. They connect to the computer’s motherboard using a SATA interface. It is quite fast, providing a high data transfer rate, which is why it is widely used for HDD and SSD.
It comes in two main sizes, 3.5-inch and 2.5-inch. Come in. 3.5-inch are used in desktop computers, and 2.5-inch are used in laptops.
3. SCSI
SCSI stands for Small Computer System Interface, which is a high-performance drive. It is connected using different types of cables, including parallel and serial cables. It is often used in high-performance applications. These drives transfer data much faster than SATA drives.
4. SSHD
SSD stands for Solid-State Hybrid Drive. It consists of a small amount of flash memory built into a conventional hard disk drive. This flash memory stores frequently accessed data, improving drive performance.
5. SMR
SMR stands for Shingled Magnetic Recording, a new HDD technology that allows HDD to store more data in a smaller space. It is slower than a traditional HDD and does not provide fast performance.
6. CMR
CMR stands for Conventional Magnetic Recording, which is the traditional technology of HDD. These drives are much faster than SMR drives. Its performance is very good, but it is a bit expensive.
How HDDs Work
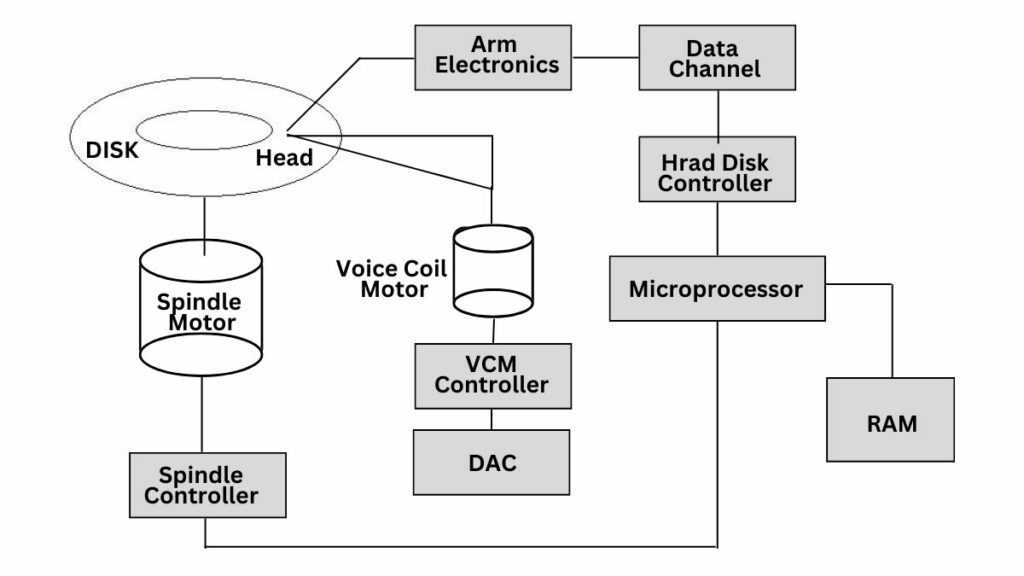
Magnetic Storage
The platter is a circular, flat disk made of non-magnetic material such as aluminum or glass coated with a thin layer of magnetic material. This magnetic coating is divided into small domains, each of which has two is magnetized in one of the directions. These platters store the data.
Platters and Heads
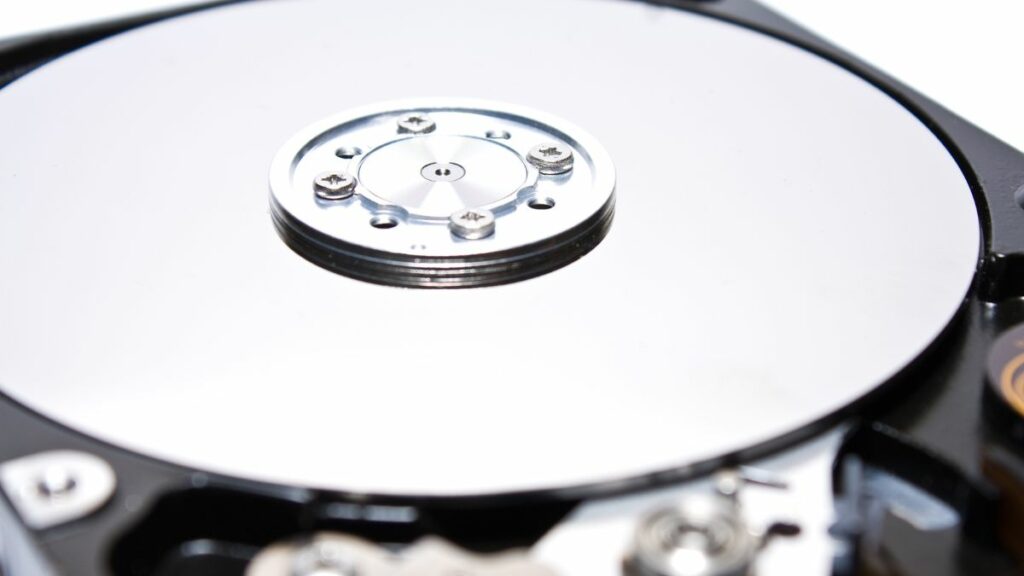

There is a read/write head on the surface of the platter. Each platter has its own head. These heads are mounted on a moving actuator arm that positions them on the desired track on the platter. These heads are very close to the surface of the rotating platter but do not touch it.
Data is stored as magnetic patterns on platters. These patterns represent binary data, with one magnetic state corresponding to 0 and the opposite state corresponding to 1. Read/write heads generate magnetic fields to write data onto the platters or detect magnetic positions to read data.
Reading and Writing Data
To read the data, the read head passes over the platter, detects the magnetic orientation of the particles, and translates them into binary data. Then, it converts this information into electrical signals, which are further interpreted by the drive’s electronics to retrieve the original binary data.
To write data, the write head creates a magnetic field that aligns the magnetic particles on the platter’s surface. This determines the alignment data value. Changes the magnetic orientation of specific areas on the platter in writing data.
Spindle and Motor
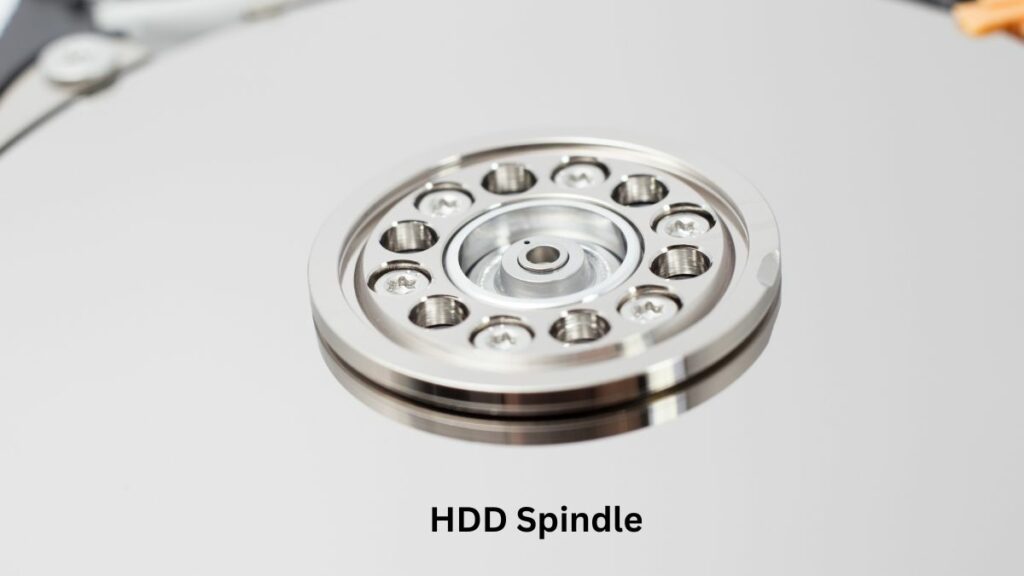

The spindle is a metal rod or shaft directly connected to the motor. It passes through the center of the hard drive and connects to the platters.
The motor rotates the spindle, causing the platters mounted on the spindle to rotate at high speed. The speed of the motor is controlled by the hard drive’s electronics and firmware.
The rotating motion sets the plates in motion, and they rotate at a consistent speed, measured in RPM ranging from 5,400 to 7,200. The rotation speed of the platters is an important factor in determining the performance of a hard drive. The faster the platter speed, the faster the data access.
Control Circuitry
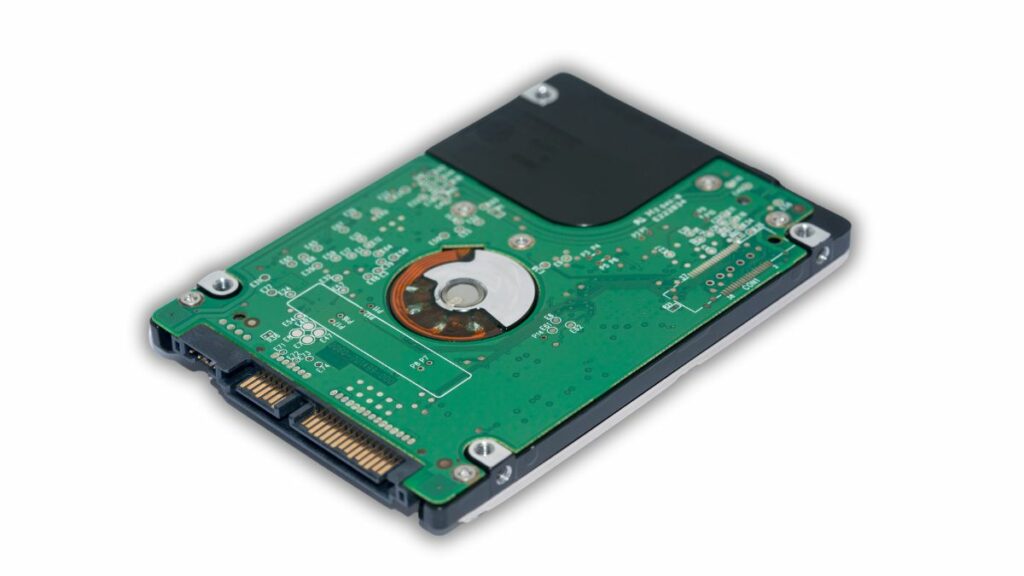

The controller board also called a logic board or PCB, is the critical component of the HDD that houses the control circuitry. It plays a vital role in coordinating all the functions of the HDD, ensuring smooth and efficient data storage and retrieval. Apart from the controller chip, there are many other integrated circuits. It acts as the brain of the HDD.
Data Organization
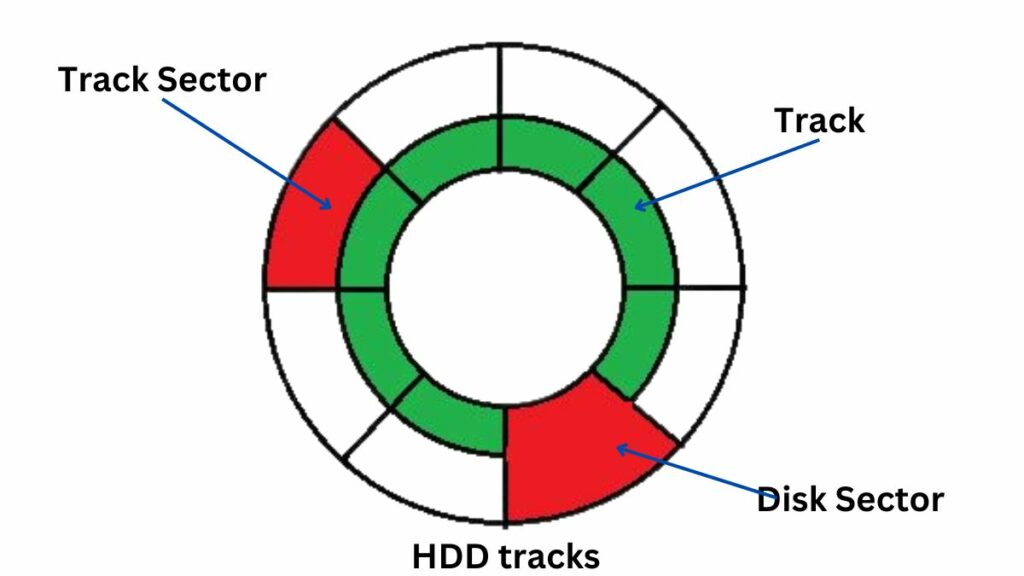
Data is arranged in concentric circles on platters called tracks. Each track is divided into sectors, which are the smallest storage units. The read/write head rotates across the platters, positioning itself on specific tracks and sectors to access data. The combination of tracks and sectors creates a grid-like structure for data storage.
Advantages of HDDs
Affordability
HDDs are usually cheaper than SSDs and come with more storage, meaning if you spend a little money and buy an SSD with less storage, you will get an HDD with more storage for the same money.
Reliability
HDD has moving parts, yet it is more reliable than SSD. If you use it with proper care, it can last for a long time. Also, data recovery is easier than SSD in case of HDD failure.
High Capacities
HDDs come with a very large storage capacity, ranging from several hundred gigabytes to several terabytes. At the same time, SSD comes only to a few Tera bytes. That’s why HDD is chosen when it comes to large storage.
Disadvantages of HDDs
Slower Speeds
HDDs have slower read and write speeds than SSDs. Due to this, it takes more time to boot, and application loading is also slow. Its slower performance makes a difference to the performance of the entire system.
More Power Consumption
HDDs consume more power than SSDs. Because there are mechanical parts inside it like plates, spines, read/write heads, actuator arms, etc., which require more power to run.
Noise and Heat Generation
Since there are moving parts inside the HDD and it generates noise during operation, they move continuously, which also generates heat.
Bulkier and Heavier
HDD has many mechanical parts, which makes it heavier than SSD. Due to this, it is not good for portable devices.
Limited Lifespan
There are moving parts inside the HDD that keep rotating and working continuously, which can cause wear and tear over time and damage the HDD.
Also Read: Best SSD Laptops
Applications of HDDs
Personal Computing
HDD is used in personal computing desktop and laptop computers because it comes with more storage, and it is easy to recover data from it in case of an HDD failure. Hence, it is the first choice of people in personal computing.
Data Centers
Since HDDs come with a very large storage capacity, they are used to store large amounts of data for various purposes, including cloud storage, web hosting, and data analytics.
Backup Purposes
While it is tough to recover data in case of SSD failure, it is easy to recover data from HDD. Hence, it is used to protect data from loss.
Media and Entertainment
Because HDD can easily store very large files, it is used in production studios, film archives, and music libraries to store films, music, and other multimedia content.
Surveillance Systems
CCTV cameras record continuously, which requires a high-capacity storage device; that is why HDD stores video records in most surveillance systems.
HDD vs. Other Storages
HDD VS SSD
| Feature | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSD (Solid State Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Mechanical | Solid State |
| Components | Also Larger Capacity but not the same as HDDs | NAND-based flash memory |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Durability | Less Durable due to Mechanical Parts Failure | More durable, No moving parts |
| Reliability | Less reliable | Generally more reliable |
| Form Factor | Larger and heavier | Smaller and lighter |
| Noise | More noise due to moving parts | Silent |
| Heat | Generates more heat | Generates less heat |
| Capacity | Larger storage | Also Larger Capacity but not same as HDDs |
| Price | Generally more cost-effective for larger capacities | More expensive, especially at higher capacities |
| Power Consumption | Consumes more power | Lower power consumption |
| Boot and Load Times | Slower boot times and application loading | Faster boot times and quicker application loading |
| Lifespan and Endurance | longer lifespan but can fail due to mechanical Parts | Limited write endurance |
Learn More: SSD vs HDD: What’s the Difference?
HDD VS eMMC

| Feature | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | eMMC (Embedded MultiMediaCard) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Mechanical | NAND-based flash memory |
| Components | Faster than traditional HDDs | NAND flash memory |
| Speed | Slower | Faster then traditional HDDs |
| Durability | Less Durable due to Mechanical Parts Failure | More durable |
| Reliability | Less reliable | More reliable |
| Form Factor | Larger and heavier | Compact, soldered onto the motherboard in a small chip |
| Noise | More noise due to moving parts | Quieter |
| Heat | Generates more heat | Generates less heat |
| Capacity | Larger storage | Much Less Capacity than HDDs |
| Price | Generally more cost-effective for larger capacities | similar or slightly more expensive than HDDs |
| Power Consumption | Consumes more power | Less power consumption |
| Boot and Load Times | Slower boot times and application loading | Faster boot times and quicker application loading |
| Lifespan and Endurance | longer lifespan but can fail due to mechanical Parts | Limited write endurance, designed for lighter workloads |
Learn More: What is eMMC: Everything You Need to Know
HDD VS SSHD
| Feature | HDD (Hard Disk Drive) | SSHD (Solid State Hybrid Drive) |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Mechanical | Hybrid (Mechanical + NAND Flash) |
| Components | Spinning platters, read/write heads, Spindle, Actuator Arm, Controller Board | Spinning platters, NAND flash memory cache |
| Speed | Slower | Faster access to frequently |
| Durability | Less Durable due to Mechanical Parts Failure | More durable than HDDs |
| Reliability | Less reliable | Enhanced reliability compared to traditional HDDs |
| Form Factor | Larger and heavier | Similar to HDDs |
| Noise | More noise due to moving parts | Quieter |
| Heat | Generates more heat | Generates less heat |
| Capacity | Larger storage | Similar Capacity to HDDs |
| Price | Generally more cost-effective for larger capacities | Moderately priced, falls between HDDs and SSDs |
| Power Consumption | Consumes more power | Consumes less power than HDDs |
| Boot and Load Times | Slower boot times and application loading | Faster boot times and quicker access to cached data |
| Lifespanand Endurance | longer lifespan but can fail due to mechanical Parts | Enhanced endurance compared to traditional HDDs |
How To Choose the Right HDDs

Before buying an HDD, identify your requirements and how much storage you need because HDDs come with very large storage capacities ranging from a few hundred gigabytes to several terabytes.
Consider the performance requirements. If you need fast data access and system responsiveness, we recommend purchasing an SSD, but an HDD would be better suited if you need more storage than performance.
A standard HDD is a cost-effective option if you need storage for everyday computing tasks, general file storage, or backup purposes. But if you need high-speed access for gaming, video editing, or other performance-intensive tasks, then an SSD or hybrid drive will be a good option.
Budget is the biggest factor in purchasing any device. HDDs are generally cheaper than SSDs. If your budget is very low and you need more storage, then HDD will still be a good option.
HDDs come in different form factors, usually with 3.5-inch drives for desktops and 2.5-inch drives for laptops and external drives. Therefore, choose an HDD that fits in the slot of your computer and laptop.
Generally, HDD has more reliability, and it is also more accessible to backup data. If you need a storage device for a long time, you can make HDD the first choice.
Before purchasing an HDD, make sure whether the interface of the HDD is compatible with your system or not. They come with SATA for traditional HDDs, SSDs, and SAS (Serial Attached SCSI) interfaces for enterprise-level drives. Check your system’s specifications to see which interfaces your system supports.
Always choose HDD with maximum cache size. The cache size of the HDD affects the performance of your system. Always buy an HDD with a larger cache size because if the cache size is larger, then the performance of your system will be better.
Also, pay attention to which brand of HDD is good in the market because good brands use high-quality materials in making HDD, which increases the reliability of HDD. Some good brands, like Seagate, Western Digital, Toshiba, Intel, SanDisk, etc., make good-quality HDDs.
Also Read: What to Look for in a Computer?
Final Word
Digital storage technologies are constantly evolving, with SSDs providing great performance nowadays, but HDDs remain a ubiquitous and reliable storage solution. Because it comes with large storage, it is used in personal computers, data centers, and various applications. It is also budget-friendly as it provides more storage at a lower budget.
HDDs have moving parts that consume more power and heat and generate noise compared to SSDs. While SSD provides faster data access and better system response, HDD is a little slower than SSD, but its lifespan is longer than SSD, and data recovery from it is easier than SSD. Its moving parts may fail, but there will be no problem recovering data.
Before buying an HDD and SSD, consider your requirements and buy a storage device that will last a long time.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using an HDD?
HDDs come out cheaper as they provide more storage per dollar than SSDs. Also, it comes with more storage capacity. SSDs have advanced a lot but still come with much less storage than HDDs.
How many types of HDD are there?
There are many types of HDDs but the most prominent among them are Desktop HDDs which are used for general storage in personal computers, NAS HDDs which are designed for Network Attached Storage (NAS) devices, Enterprise HDDs which come with very high capacity and are used in data centers and servers, Surveillance HDDs which are used to store the recordings of CCTV cameras.
How to increase HDD speed?
Although the speed of HDD depends on many factors, there are some important things which can be done to increase its speed like deleting temporary files, Defragmenting your HDD, enabling write caching, optimizing background services, apps and storage space, By scanning your hard drive for bad sectors and deleting junk data. Doing all these things increases HDD by approx.
Does HDD speed affect system performance?
Yes, HDD speed matters which affects system performance. The speed of an HDD affects the time it takes to access and transfer data. Higher speed drives generally provide faster performance, resulting in faster file access and data transfer speeds leading to better system performance.
What is defragmentation of HDD?
Defragmentation of HDD is a process used to optimize the arrangement of data stored on the disk. Over time, as files are created, modified, and deleted, parts of the same file become scattered across different physical locations on disk.
reorganizes these files and consolidates them into contiguous blocks, improving access times and overall system performance. This process helps reduce the time taken to read and write data to the disk by reducing the distance traveled by the read/write heads.




