The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the primary component of any computer system. It executes the functions, programs, and software instructions.
With the right CPU, your computer will perform tasks smoothly and efficiently. When you purchase a new desktop, laptop, or build your own PC, choosing the right CPU is one of the most important decisions.
Selecting a processor for any computer or laptop can be challenging because there are many options available in the market.
But don’t worry!
In this guide, we’ll cover the main specifications and factors to consider when selecting a CPU for your needs.
- What is a CPU?
- Important components to look for in a CPU?
- FAQs
What is a CPU?
A Central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
It plays a crucial role in determining the computer’s overall performance. When choosing a CPU, several key factors must be considered.
The Important components to look for in a CPU?
1. CPU Cores and Threads
Cores and threads are fundamental CPU components.
The core represents an individual or central processing unit within the CPU, while threads allow each core to handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
More cores and threads generally lead to better multitasking performance.
Modern CPUs come with Multiple cores, allowing them to handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Dual-core
- Quad-core
- Hexa- core
- Octa-core CPUs are common.
Consider your specific needs; more cores can significantly boost performance if you’re into gaming or content creation.
Hyper-Threading technology enables each core to work on two threads simultaneously, enhancing the performance of a computer. It’s a valuable feature for users who frequently run multiple applications concurrently.
2. Clock Speed and Performance
Clock speed, measured in GHz, determines how quickly the CPU can execute instructions.
Higher clock speeds typically result in better overall performance, but other factors, such as architecture, can influence this.
It’s essential to balance clock speed and other factors, such as the number of cores, threads, and generation.
Cache Size
CPU cache stores frequently accessed data, reducing the time it takes to fetch information. A CPU cache is a small, high-speed memory that stores frequently used data.
A larger cache size can improve performance, especially for tasks involving large datasets.
Cache memory in a CPU:
- L1: Fastest, stores frequently used data.
- L2: Slightly larger, shared among cores.
- L3: Larger, shared among all cores, reduces memory access time.
The L1, L2, and L3 cache are memory buffers that store data closer to the CPU cores. This allows the processor to access frequently used data more quickly than retrieving it from the slower system memory.
This hierarchy of cache memory helps improve a CPU’s overall speed and efficiency.
3. Compatibility and Socket Types
When you choose a CPU, compatibility with your existing hardware or the hardware you will purchase is crucial.
The socket type refers to the physical interface on a computer’s motherboard that connects the central processing unit (CPU).
It determines the compatibility between the CPU and the motherboard, as different socket types are designed for specific CPU models and generations.
Several socket types are available, each associated with CPU manufacturers and families. Some commonly used socket types include:
- Intel: LGA1151, LGA1200, LGA2066
- AMD: AM4, TR4, sTRX4
It is essential to ensure that the CPU and motherboard have the same socket type to ensure compatibility.
Before purchasing a CPU, it is recommended to check the motherboard’s specifications to determine the compatible socket type.
The chipset on the motherboard determines the features and capabilities it supports. Ensure the motherboard’s chipset is compatible with the CPU you plan to use.
For example, if you have a Raptor Lake Intel 13th generation CPU, you need a motherboard with a compatible Intel 600 or 700 series chipset.
Different CPUs have different power requirements. Ensure that the motherboard can deliver the necessary power to the CPU. This includes having the appropriate power connectors and sufficient power phases for stable operation.
The motherboard’s BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) needs to support the specific CPU you plan to use. The motherboard must have a BIOS version with the necessary microcode updates for proper CPU recognition and compatibility. You may need to update the motherboard’s BIOS before installing a newer CPU.
Consider the form factor of the motherboard, such as ATX, microATX, or Mini-ITX, and ensure that it fits in your computer case. Different form factors have different physical dimensions and mounting hole placements.
4. TDP (Thermal Design Power)
TDP is crucial, as it determines how much heat your CPU generates and how much cooling it requires. Select a CPU with a TDP suitable for your cooling solution.
TDP indicates how much heat a CPU generates under maximum load. Lower TDP CPUs are more power-efficient and produce less heat, which is ideal for smaller form-factor builds or energy-conscious users.
5. Usage Scenarios
Gaming

Gamers should prioritize CPUs with high clock speeds and multiple cores for smooth gameplay. Compatibility with the latest games is also crucial.
With the latest generation of Intel or AMD CPU, you can easily play modern games like Cyberpunk 2077, Valorant, Red Dead Redemption 2, etc., at high FPS.
Content Creation
Content creators benefit from CPUs with a balance of high core counts and strong single-threaded performance. This ensures efficient video editing, rendering, and multitasking.
Tasks such as rendering high-resolution videos like 4K or 8K demand significant CPU power, so selecting a better and more powerful processor is ideal.
Office Tasks
A budget-friendly CPU with basic features is usually sufficient for office tasks and everyday computing. If your laptop or computer has the latest Intel Core i3, i5 or AMD Ryzen 3, Ryzen 5 then office work will be done easily.
Budget-Friendly Options
For budget-conscious users, entry-level CPUs from both Intel and AMD offer good value for everyday tasks like web browsing, document editing, and light gaming.
Mid-Range Power
Mid-range CPUs balance price and performance, making them suitable for gamers, content creators, and professionals who require solid multitasking capabilities.
High-End Performance
Consider investing in a high-end CPU if you demand top-tier performance for tasks like 3D rendering, Ultra HD video editing, or gaming at ultra-high frame rates. These processors often have more cores, higher clock speeds, and advanced features.
6. Power Efficiency
Power efficiency in CPUs refers to the ability of a CPU to deliver high performance while consuming minimal power. It is an important factor to consider when evaluating a CPU’s overall performance and energy consumption.
- Design and Architecture: CPU makers enhance designs, microarchitectures, and power-saving features for better efficiency.
- Process Technology: Smaller semiconductor process nodes lead to improved energy efficiency in newer CPUs.
- Power Management: CPUs adapt power use with frequency and voltage scaling features.
- Thermal Design: Efficient cooling prevents overheating and enhances power efficiency.
- Component Selection: Choosing energy-efficient components across the system optimizes overall power usage.
7. Energy Consumption
CPUs consume electrical power, measured as Thermal Design Power (TDP). Lower TDP indicates better efficiency. Workload affects power use; heavy tasks consume more.
Power management adjusts CPU performance based on workload, optimizing energy use. Efficient cooling is crucial to prevent increased power consumption due to overheating.
8. Heat Generation
CPUs turn most of the power they use into heat. This heat needs cooling to avoid overheating and keep the CPU working well.
Cooling methods like fans and heat sinks are essential to manage heat and maintain CPU performance. Proper cooling also helps the CPU last longer and work reliably.
9. Cooling Solutions
Air cooling is a common and effective method to maintain optimal CPU temperatures. It relies on heat sinks, metal blocks with fins, to absorb and distribute heat.
Fans mounted on the heat sink blow air over the fins, cooling the CPU. This cost-effective solution is easy to install and requires minimal maintenance.
It suits most users’ needs but may need help with heavily overclocked systems or demanding workloads.
Liquid cooling, or water cooling, offers efficient CPU heat dissipation. A closed-loop system circulates coolant through tubes, transferring heat from the CPU to a radiator where a fan dissipates it.
Liquid cooling excels in cooling performance, ideal for high-performance PCs and overclocking.
It often features aesthetic elements like RGB lighting. However, it’s pricier, demands careful installation and maintenance, and carries a slightly higher risk of leaks, though modern systems are designed to minimize this risk.
10. Warranty and Support
Check the warranty and customer support options provided by the CPU manufacturer. A reliable warranty can offer peace of mind.
You also need to choose a CPU with a minimum 1-year warranty. In some processors, you will also get a 3-year warranty, which will be the best option.
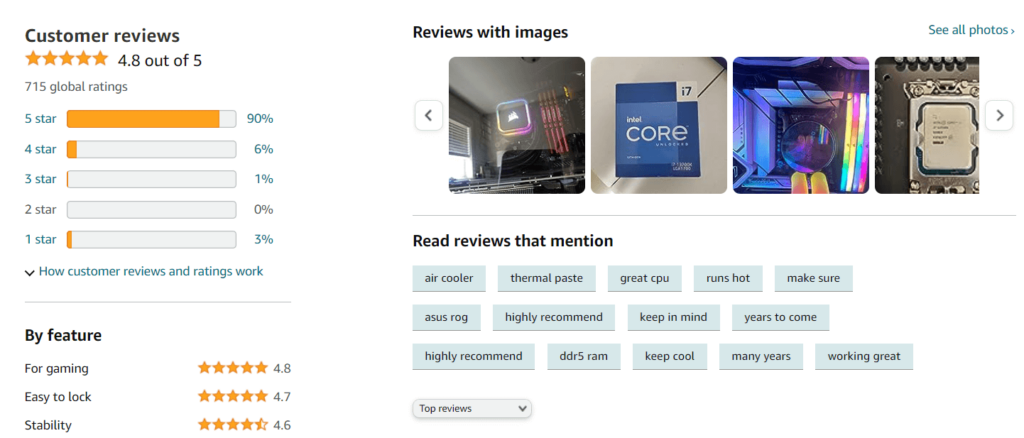
11. User Reviews and Recommendations
Before making a final decision, read user reviews and seek recommendations from trusted sources, forums, and online communities.
You can easily check reviews and customer care ratings online. Always choose a 4+ star CPU.
FAQs
No, Intel CPUs are incompatible with AMD motherboards and vice versa. Always match the CPU and motherboard from the same manufacturer.
For gaming, a CPU with a TDP of 65 watts or lower is generally considered ideal. It balances performance and power efficiency.
The CPU plays a crucial role in gaming performance, especially in games that rely heavily on physics simulations and AI. A powerful CPU can reduce bottlenecks and deliver smoother gameplay.
It depends on the motherboard’s socket type. Some motherboards support CPU upgrades within the same socket type, but you should always check compatibility with your motherboard manufacturer.
It depends on your usage. Integrated graphics are suitable for basic tasks, but a dedicated graphics card is recommended for gaming or graphic-intensive work.
Not necessarily. While higher clock speeds indicate faster performance, other factors, like the number of cores and cache size, also play a significant role. It’s essential to consider the overall CPU specifications.